FXR agonist INT-747 upregulates DDAH expression and enhances insulin sensitivity in high-salt fed Dahl rats
- PMID: 23593273
- PMCID: PMC3617194
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060653
FXR agonist INT-747 upregulates DDAH expression and enhances insulin sensitivity in high-salt fed Dahl rats
Abstract
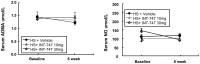
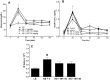
Aims: Genetic and pharmacological studies have shown that impairment of the nitric oxide (NO) synthase (NOS) pathway is associated with hypertension and insulin-resistance (IR). In addition, inhibition of NOS by the endogenous inhibitor, asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), may also result in hypertension and IR. On the other hand, overexpression of dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH), an enzyme that metabolizes ADMA, in mice is associated with lower ADMA, increased NO and enhanced insulin sensitivity. Since DDAH carries a farnesoid X receptor (FXR)-responsive element, we aimed to upregulate its expression by an FXR-agonist, INT-747, and evaluate its effect on blood pressure and insulin sensitivity.
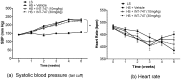
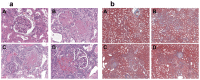
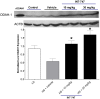
Methods and results: In this study, we evaluated the in vivo effect of INT-747 on tissue DDAH expression and insulin sensitivity in the Dahl rat model of salt-sensitive hypertension and IR (Dahl-SS). Our data indicates that high salt (HS) diet significantly increased systemic blood pressure. In addition, HS diet downregulated tissue DDAH expression while INT-747 protected the loss in DDAH expression and enhanced insulin sensitivity compared to vehicle controls.
Conclusion: Our study may provide the basis for a new therapeutic approach for IR by modulating DDAH expression and/or activity using small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatic dimethylarginine-dimethylaminohydrolase1 is reduced in cirrhosis and is a target for therapy in portal hypertension.J Hepatol. 2015 Feb;62(2):325-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.024. Epub 2014 Aug 23. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25152204 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of high salt independent of blood pressure on PRMT/ADMA/DDAH pathway in the aorta of Dahl salt-sensitive rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Apr 12;14(4):8062-72. doi: 10.3390/ijms14048062. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23584024 Free PMC article.
-
Obeticholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, improves portal hypertension by two distinct pathways in cirrhotic rats.Hepatology. 2014 Jun;59(6):2286-98. doi: 10.1002/hep.26939. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 24259407
-
Modulating DDAH/NOS Pathway to Discover Vasoprotective Insulin Sensitizers.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:1982096. doi: 10.1155/2016/1982096. Epub 2015 Dec 6. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 26770984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH): expression, regulation, and function in the cardiovascular and renal systems.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Dec;293(6):H3227-45. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00998.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17933965 Review.
Cited by
-
DDAH1 Protects against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Hepatoxicity in Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 29;11(5):880. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050880. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624743 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acid receptors and renal regulation of water homeostasis.Front Physiol. 2023 Nov 15;14:1322288. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1322288. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38033333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psyllium Fiber Protects Against Colitis Via Activation of Bile Acid Sensor Farnesoid X Receptor.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;15(6):1421-1442. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.02.007. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36828279 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic dimethylarginine-dimethylaminohydrolase1 is reduced in cirrhosis and is a target for therapy in portal hypertension.J Hepatol. 2015 Feb;62(2):325-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.024. Epub 2014 Aug 23. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25152204 Free PMC article.
-
Role of FXR in Renal Physiology and Kidney Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 26;24(3):2408. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032408. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- He FJ, MacGregor GA (2010) Reducing population salt intake worldwide: from evidence to implementation. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 52: 363–382. - PubMed
-
- Cianciaruso B, Bellizzi V, Minutolo R, Tavera A, Capuano A, et al. (1998) Salt intake and renal outcome in patients with progressive renal disease. Miner Electrolyte Metab 24: 296–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

