miRNA-27b targets vascular endothelial growth factor C to inhibit tumor progression and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 23593282
- PMCID: PMC3625233
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060687
miRNA-27b targets vascular endothelial growth factor C to inhibit tumor progression and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most prevalent cancers globally and is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths due to therapy resistance and metastasis. Understanding the mechanism underlying colorectal carcinogenesis is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of CRC. microRNAs (miRNAs) can act as either oncogenes or tumor suppressors in many cancers. A tumor suppressor role for miR-27b has recently been reported in neuroblastoma, while no information about miR-27b in CRC is available. In this study, we demonstrated that miR-27b expression is decreased in most CRC tissues and determined that overexpression of miR-27b represses CRC cell proliferation, colony formation and tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. We identified vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) as a novel target gene of miR-27b and determined that miR-27b functioned as an inhibitor of tumor progression and angiogenesis through targeting VEGFC in CRC. We further determined that DNA hypermethylation of miR-27b CpG islands decreases miR-27b expression. In summary, an anti-tumor role for miR-27b and its novel target VEGFC in vivo could lead to tumor necrosis and provide a rationale for developing miR-27b as a therapeutic agent.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
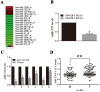
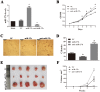
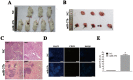
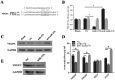

References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, et al. (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127: 2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Vo DM, Julien LA, Thorson AG (2010) Current controversies in colon and rectal cancer. Minerva Chir 65: 677–693. - PubMed
-
- Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T, Thun M (2001) Cancer statistics, 2001. CA Cancer J Clin 51: 15–36. - PubMed
-
- Mueller MM, Fusenig NE (2004) Friends or foes - bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer 4: 839–849. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F (2004) Cancer and the chemokine network. Nature Reviews Cancer 4: 540–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

