Minocycline suppresses interleukine-6, its receptor system and signaling pathways and impairs migration, invasion and adhesion capacity of ovarian cancer cells: in vitro and in vivo studies
- PMID: 23593315
- PMCID: PMC3620477
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060817
Minocycline suppresses interleukine-6, its receptor system and signaling pathways and impairs migration, invasion and adhesion capacity of ovarian cancer cells: in vitro and in vivo studies
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Minocycline Suppresses Interleukine-6, Its Receptor System and Signaling Pathways and Impairs Migration, Invasion and Adhesion Capacity of Ovarian Cancer Cells: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 2;19(2):e0298444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298444. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38306336 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
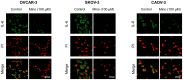
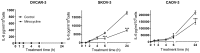
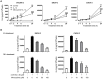
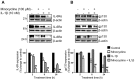
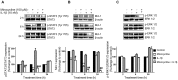
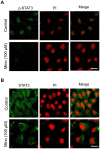
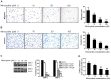
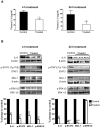
Interleukin (IL)-6 has been shown to be a major contributing factor in growth and progression of ovarian cancer. The cytokine exerts pro-tumorigenic activity through activation of several signaling pathways in particular signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT3) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2. Hence, targeting IL-6 is becoming increasingly attractive as a treatment option in ovarian cancer. Here, we investigated the effects of minocycline on IL-6 and its signaling pathways in ovarian cancer. In vitro, minocycline was found to significantly suppress both constitutive and IL-1β or 4-hydroxyestradiol (4-OH-E2)-stimulated IL-6 expression in human ovarian cancer cells; OVCAR-3, SKOV-3 and CAOV-3. Moreover, minocycline down-regulated two major components of IL-6 receptor system (IL-6Rα and gp130) and blocked the activation of STAT3 and ERK1/2 pathways leading to suppression of the downstream product MCL-1. In female nude mice bearing intraperitoneal OVCAR-3 tumors, acute administration (4 and 24 h) of minocycline (30 mg/kg) led to suppression of IL-6. Even single dose of minocycline was effective at significantly lowering plasma and tumor IL-6 levels. In line with this, tumoral expression of p-STAT3, p-ERK1/2 and MCL-1 were decreased in minocycline-treated mice. Evaluation of the functional implication of minocycline on metastatic activity revealed the capacity of minocycline to inhibit cellular migration, invasion and adhesion associated with down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 and 9. Thus, the data suggest a potential role for minocycline in suppressing IL-6 expression and activity. These effects may prove to be an important attribute to the upcoming clinical trials of minocycline in ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Maccio A, Madeddu C (2012) Inflammation and ovarian cancer. Cytokine 58: 133–147. - PubMed
-
- Guo Y, Xu F, Lu T, Duan Z, Zhang Z (2012) Interleukin-6 signaling pathway in targeted therapy for cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. - PubMed
-
- Gastl G, Plante M (2001) Bioactive interleukin-6 levels in serum and ascites as a prognostic factor in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Methods Mol Med 39: 121–123. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

