Identifying communities and key vertices by reconstructing networks from samples
- PMID: 23593375
- PMCID: PMC3622610
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061006
Identifying communities and key vertices by reconstructing networks from samples
Abstract
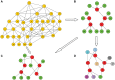
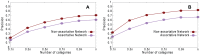
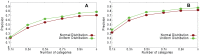
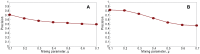
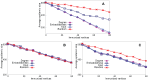
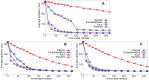
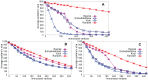
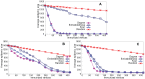
Sampling techniques such as Respondent-Driven Sampling (RDS) are widely used in epidemiology to sample "hidden" populations, such that properties of the network can be deduced from the sample. We consider how similar techniques can be designed that allow the discovery of the structure, especially the community structure, of networks. Our method involves collecting samples of a network by random walks and reconstructing the network by probabilistically coalescing vertices, using vertex attributes to determine the probabilities. Even though our method can only approximately reconstruct a part of the original network, it can recover its community structure relatively well. Moreover, it can find the key vertices which, when immunized, can effectively reduce the spread of an infection through the original network.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
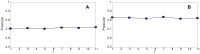
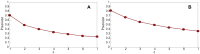
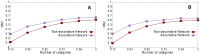
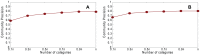
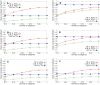
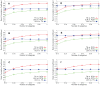
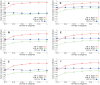
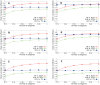
Similar articles
-
Estimation and correction of bias in network simulations based on respondent-driven sampling data.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 14;10(1):6348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63269-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32286412 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating Vertex Measures in Social Networks by Sampling Completions of RDS Trees.Soc Netw. 2015 Jan 1;4(1):1-16. doi: 10.4236/sn.2015.41001. Soc Netw. 2015. PMID: 25838988 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing respondent-driven sampling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 13;107(15):6743-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000261107. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20351258 Free PMC article.
-
More comprehensive reporting of methods in studies using respondent driven sampling is required: a systematic review of the uptake of the STROBE-RDS guidelines.J Clin Epidemiol. 2020 Jan;117:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.09.024. Epub 2019 Oct 4. J Clin Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 31589951
-
The development of respondent-driven sampling (RDS) inference: A systematic review of the population mean and variance estimates.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020 Jan 1;206:107702. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.107702. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020. PMID: 31761476
Cited by
-
THE GRAPHICAL STRUCTURE OF RESPONDENT-DRIVEN SAMPLING.Sociol Methodol. 2016;46(1):187-211. doi: 10.1177/0081175016641713. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Sociol Methodol. 2016. PMID: 31607761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lü L, Zhou T (2011) Link prediction in complex networks: a survey. Physica A 390: 1150–1170.
-
- Leskovec J, Huttenlocher D, Kleinberg J (2010) Predicting positive and negative links in online social networks. In: WWW 2010: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web. Raleigh, North Carolina, USA, pp 641–650.
-
- Guo F, Yang Z, Zhou T (2012) Predicting link directions via a recursive subgraph-based ranking. Available: arXiv 1206.2199.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

