Leptomeningeal metastases in breast cancer
- PMID: 23593536
- PMCID: PMC3623833
Leptomeningeal metastases in breast cancer
Abstract
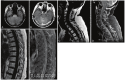
Central nervous system (CNS) metastasis from breast cancer may be characterized as either parenchymal brain metastasis (BM) or leptomeningeal (LM) metastasis. BM are much more common (about 80% of all CNS metastases), and have been more extensively studied than LM. CNS metastasis in breast cancer has been associated with reduced overall survival, with the shortest survival generally observed in cases of LM. Here, we review the epidemiology, prognostic factors, diagnostic tools, currently available treatments, and potential future therapies for LM from breast cancer.
Keywords: Leptomeningeal metastases; breast cancer; intrathecal chemotherapy.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
