The use of trigger point dry needling and intramuscular electrical stimulation for a subject with chronic low back pain: a case report
- PMID: 23593553
- PMCID: PMC3625794
The use of trigger point dry needling and intramuscular electrical stimulation for a subject with chronic low back pain: a case report
Abstract
Study design: Case Report.
Background and purpose: Myofascial trigger points (MTrPs) are widely accepted by clinicians and researchers as a primary source of regional neuromusculoskeletal pain. Trigger point dry needling (TrP-DN) is an invasive procedure that involves stimulation of MTrPs using an monofilament needle. The purpose of this case report is to report the outcomes of TrP-DN and intramuscular electrical stimulation (IES) as a primary treatment intervention in a subject with chronic low back pain.
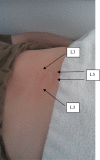
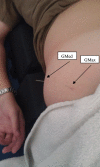
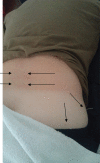
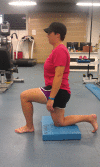
Case description: The subject was a 30-year-old female, active duty military, who was referred to physical therapy for low back and right posterolateral hip pain. She noticed symptoms after suffering a lumbar flexion injury while picking up a barbell during weight training. Physical examination demonstrated findings that supported the diagnosis of lumbar segmental instability with a right hip stability dysfunction. Objective findings included a multi-segmental flexion movement pattern dysfunction and MTrPs in the right gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles with deep palpation. The subject was treated with TrP-DN and IES for a total of two visits. Bilateral L3 and L5 multifidus and right gluteus maximus and medius muscles were treated, along with implementing a home exercise program consisting of core stability exercises.
Outcomes: The subject reported no existing pain and disability on the Numerical Pain Rating Scale and Oswestry Disability Questionnaire and a large perceived change in recovery on the Global Rating of Change at final follow-up. Physical examination was normal, demonstrating no observed impairments or functional limitations, including normal multi-segmental flexion and no MTrPs with deep palpation.
Discussion: The subject was able to return to full military active duty without any physical limitations and resumed pre-injury activity levels, including the ability to resume all activities without pain. There is much promise regarding the use of TrP-DN with IES intervention for the treatment of lumbar and/or hip stability dysfunction. Future research is recommended to determine if TrP-DN intervention, with and without IES, is effective for other body regions and long-term subject outcomes.
Level of evidence: Level 4.
Keywords: Dry needling; intramuscular electrical stimulation; low back pain; myofasical trigger points.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Treatment of nonspecific thoracic spine pain with trigger point dry needling and intramuscular electrical stimulation: a case series.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2014 Oct;9(5):699-711. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2014. PMID: 25328832 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of subacute posterior knee pain in an adolescent ballet dancer utilizing trigger point dry needling: a case report.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2014 Feb;9(1):116-24. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2014. PMID: 24567862 Free PMC article.
-
The use of dry needling for a subject with acute onset of neck pain: a case report.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015 Feb;10(1):104-13. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015. PMID: 25709869 Free PMC article.
-
Dry needling: a literature review with implications for clinical practice guidelines.Phys Ther Rev. 2014 Aug;19(4):252-265. doi: 10.1179/108331913X13844245102034. Phys Ther Rev. 2014. PMID: 25143704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger Points in the Triceps Surae Muscles: Systematic Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Sep 24;10(10):1862. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10101862. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electrical dry needling versus conventional physiotherapy in the treatment of active and latent myofascial trigger points in patients with nonspecific chronic low back pain.Trials. 2022 Mar 28;23(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06179-y. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35346331 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of dry needling on lumbar muscle stiffness in patients with low back pain: A double blind, randomized controlled trial using shear wave elastography.J Man Manip Ther. 2022 Jun;30(3):154-164. doi: 10.1080/10669817.2021.1977069. Epub 2021 Sep 16. J Man Manip Ther. 2022. PMID: 34525901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
DRY NEEDLING FOR MYOFASCIAL TRIGGER POINT PAIN: A CLINICAL COMMENTARY.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015 Jun;10(3):402-18. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2015. PMID: 26075156 Free PMC article.
-
SHORT-TERM EFFECTS OF TRIGGER POINT DRY NEEDLING ON PAIN AND DISABILITY IN SUBJECTS WITH PATELLOFEMORAL PAIN SYNDROME.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2018 Jun;13(3):462-473. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2018. PMID: 30038832 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Effects of PENS versus Dry Needling in Subjects with Unilateral Mechanical Neck Pain and Active Myofascial Trigger Points in Levator Scapulae Muscle: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2020 Jun 1;9(6):1665. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061665. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32492884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tough EA, White AR. Effectiveness of acupuncture/dry needling for myofascial trigger point pain. Physical Therapy Reviews. 2011;16(2):147
-
- Tough EA, White AR, Richards S, Campbell J. Variability of criteria used to diagnose myofascial trigger point pain syndrome–evidence from a review of the literature. Clin J Pain. 2007;23:278–6 - PubMed
-
- Simons DG, Travell JG, Simons LS. Travell and Simons' myofascial pain and dysfunction: the trigger point manual. Vol.1 Upper half of the body. Baltimore: MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999
-
- Dommerholt J. Muscle pain syndromes. In: Myofascial Manipulation. Cantu RI, Grodin AJ, ed. Gaithersburg, Md:Aspen; 2001:93–140
-
- Dommerholt J. Dry needling in orthopedic physical therapy practice. Orthop Phys Ther Pract. 2004;16(3):15–20
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
