A study of hepatitis B virus reactivation associated with rituximab therapy in real-world clinical practice: a single-center experience
- PMID: 23593610
- PMCID: PMC3622856
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2013.19.1.51
A study of hepatitis B virus reactivation associated with rituximab therapy in real-world clinical practice: a single-center experience
Abstract
Background/aims: The widespread use of cytotoxic chemotherapy and immunosuppressants has resulted in reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) recently becoming an issue. Although rituximab (an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) has revolutionized the treatment of lymphoma, recent reports have suggested that rituximab therapy increases the risk of viral-mediated complications, and particularly HBV reactivation. This study analyzed real clinical practice data for rituximab-related HBV reactivation.
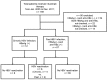
Methods: Between January 2005 and December 2011, 169 patients received treatment with rituximab. Screening status of the HBV infection and frequency of preemptive therapy were determined in these patients, and the clinical features of HBV reactivation were analyzed.
Results: Seventy-nine of the 169 patients with chronic or past HBV infection were selected for evaluation of HBV reactivation. Of the 90 patients who were excluded, 22 (13.0%) were not assessed for HBsAg and anti-HBc, and 14 (8.3%) were not assessed for anti-HBc due to seronegativity for HBsAg. The selected patients were divided into those with chronic HBV infection (n=12) and those with past HBV infection (n=67); six patients (7.6%) experienced HBV reactivation. Eight patients received preemptive therapy, but three patients (37.5%) underwent HBV reactivation. Although HBsAg seropositivity was an independent risk factor for HBV reactivation (P=0.038), of the six patients with HBV reactivation, two (33.3%) had past HBV infection and three (50%) died of liver failure.
Conclusions: The findings of this study demonstrate that adherence to guidelines for screening and preemptive therapy for HBV reactivation was negligent among the included cohort. Attention should be paid to HBV reactivation in patients with past as well as chronic HBV infection during and after rituximab therapy.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus; Immunosuppressant; Rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in hepatitis B surface antigen negative/hepatitis B core antibody positive patients receiving rituximab-containing combination chemotherapy without routine antiviral prophylaxis.Ann Hematol. 2011 Oct;90(10):1219-23. doi: 10.1007/s00277-011-1241-0. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Ann Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21520001
-
Hepatitis B reactivation in patients with previous hepatitis B virus exposure undergoing rituximab-containing chemotherapy for lymphoma: a prospective study.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Nov 20;32(33):3736-43. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.7081. Epub 2014 Oct 6. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25287829
-
Hepatitis B virus reactivation in lymphoma patients with prior resolved hepatitis B undergoing anticancer therapy with or without rituximab.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Feb 1;27(4):605-11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.0182. Epub 2008 Dec 15. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19075267
-
Reactivation of hepatitis B virus following rituximab-plus-steroid combination chemotherapy.J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jan;46(1):9-16. doi: 10.1007/s00535-010-0331-4. Epub 2010 Oct 6. J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 20924616 Review.
-
Screening for and management of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients treated with anti-B-cell therapy.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014 Dec 5;2014(1):576-83. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2014.1.576. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014. PMID: 25696914 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B virus reactivation during temozolomide administration for malignant glioma.Int J Clin Oncol. 2021 Feb;26(2):305-315. doi: 10.1007/s10147-020-01814-7. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Int J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33118116
-
Management of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Malignant Lymphoma Prior to Immunosuppressive Treatment.J Pers Med. 2021 Apr 2;11(4):267. doi: 10.3390/jpm11040267. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33918206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Patients Treated With Imatinib.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 22;10:596500. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.596500. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33552970 Free PMC article.
-
[Efficacy and safety of rituximab-contained regimen for refractory and relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a retrospective study of 10 cases].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Oct 14;39(10):855-858. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2018.10.013. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30369208 Free PMC article. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
Hepatitis B virus reactivation in HBsAg-negative, anti-HBc-positive patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy: a systematic review.Ann Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul-Aug;31(4):480-490. doi: 10.20524/aog.2018.0266. Epub 2018 Apr 28. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29991894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai CL, Yuen MF. Chronic hepatitis B--new goals, new treatment. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2488–2491. - PubMed
-
- Gürcan HM, Keskin DB, Stern JN, Nitzberg MA, Shekhani H, Ahmed AR. A review of the current use of rituximab in autoimmune diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009;9:10–25. - PubMed
-
- Yeo W, Johnson PJ. Diagnosis, prevention and management of hepatitis B virus reactivation during anticancer therapy. Hepatology. 2006;43:209–220. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe M, Shibuya A, Tsunoda Y, Danbara M, Ishii R, Ohsaka M, et al. Re-appearance of hepatitis B virus following therapy with rituximab for lymphoma is not rare in Japanese patients with past hepatitis B virus infection. Liver Int. 2011;31:340–347. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous