Drug-loaded nanoparticle systems and adult stem cells: a potential marriage for the treatment of malignant glioma?
- PMID: 23594406
- PMCID: PMC3717302
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.937
Drug-loaded nanoparticle systems and adult stem cells: a potential marriage for the treatment of malignant glioma?
Abstract
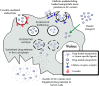
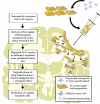
Despite all recent advances in malignant glioma research, only modest progress has been achieved in improving patient prognosis and quality of life. Such a clinical scenario underscores the importance of investing in new therapeutic approaches that, when combined with conventional therapies, are able to effectively eradicate glioma infiltration and target distant tumor foci. Nanoparticle-loaded delivery systems have recently arisen as an exciting alternative to improve targeted anti-glioma drug delivery. As drug carriers, they are able to efficiently protect the therapeutic agent and allow for sustained drug release. In addition, their surface can be easily manipulated with the addition of special ligands, which are responsible for enhancing tumor-specific nanoparticle permeability. However, their inefficient intratumoral distribution and failure to target disseminated tumor burden still pose a big challenge for their implementation as a therapeutic option in the clinical setting. Stem cell-based delivery of drug-loaded nanoparticles offers an interesting option to overcome such issues. Their ability to incorporate nanoparticles and migrate throughout interstitial barriers, together with their inherent tumor-tropic properties and synergistic anti-tumor effects make these stem cell carriers a good fit for such combined therapy. In this review, we will describe the main nanoparticle delivery systems that are presently available in preclinical and clinical studies. We will discuss their mechanisms of targeting, current delivery methods, attractive features and pitfalls. We will also debate the potential applications of stem cell carriers loaded with therapeutic nanoparticles in anticancer therapy and why such an attractive combined approach has not yet reached clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
“The authors declare that they have no competing interests.”
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, Hau P, Brandes AA, Gijtenbeek J, Marosi C, Vecht CJ, Mokhtari K, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. The lancet oncology. 2009;10(5):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Pardridge WM. Molecular biology of the blood-brain barrier. Molecular biotechnology. 2005;30(1):57–70. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai AK, Eisenberg JB, Pardridge WM. Absorptive-mediated endocytosis of cationized albumin and a beta-endorphin-cationized albumin chimeric peptide by isolated brain capillaries. Model system of blood-brain barrier transport. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1987;262(31):15214–15219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

