Identification of rare variants from exome sequence in a large pedigree with autism
- PMID: 23594493
- PMCID: PMC3722055
- DOI: 10.1159/000346560
Identification of rare variants from exome sequence in a large pedigree with autism
Abstract
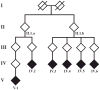
We carried out analyses with the goal of identifying rare variants in exome sequence data that contribute to disease risk for a complex trait. We analyzed a large, 47-member, multigenerational pedigree with 11 cases of autism spectrum disorder, using genotypes from 3 technologies representing increasing resolution: a multiallelic linkage marker panel, a dense diallelic marker panel, and variants from exome sequencing. Genome-scan marker genotypes were available on most subjects, and exome sequence data was available on 5 subjects. We used genome-scan linkage analysis to identify and prioritize the chromosome 22 region of interest, and to select subjects for exome sequencing. Inheritance vectors (IVs) generated by Markov chain Monte Carlo analysis of multilocus marker data were the foundation of most analyses. Genotype imputation used IVs to determine which sequence variants reside on the haplotype that co-segregates with the autism diagnosis. Together with a rare-allele frequency filter, we identified only one rare variant on the risk haplotype, illustrating the potential of this approach to prioritize variants. The associated gene, MYH9, is biologically unlikely, and we speculate that for this complex trait, the key variants may lie outside the exome.
Copyright © 2013 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures




Similar articles
-
GIGI: an approach to effective imputation of dense genotypes on large pedigrees.Am J Hum Genet. 2013 Apr 4;92(4):504-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.02.011. Am J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23561844 Free PMC article.
-
A haplotype-based framework for group-wise transmission/disequilibrium tests for rare variant association analysis.Bioinformatics. 2015 May 1;31(9):1452-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu860. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25568282 Free PMC article.
-
Multipoint linkage analysis with many multiallelic or dense diallelic markers: Markov chain-Monte Carlo provides practical approaches for genome scans on general pedigrees.Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Nov;79(5):846-58. doi: 10.1086/508472. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Am J Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 17033961 Free PMC article.
-
MYH9-related disease: description of a large Chinese pedigree and a survey of reported mutations.Acta Haematol. 2014;132(2):193-8. doi: 10.1159/000356681. Acta Haematol. 2014. PMID: 24643058 Review.
-
MYH9 related platelet disorders - often unknown and misdiagnosed.Klin Padiatr. 2011 May;223(3):120-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1275664. Epub 2011 May 12. Klin Padiatr. 2011. PMID: 21567368 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Applications of Whole Exome Sequencing Technology.Psychiatry Investig. 2016 May;13(3):255-64. doi: 10.4306/pi.2016.13.3.255. Epub 2016 May 18. Psychiatry Investig. 2016. PMID: 27247591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Candidate Variants in Two Multigenerational Families with Childhood Apraxia of Speech.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 27;11(4):e0153864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153864. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27120335 Free PMC article.
-
A unified test of linkage analysis and rare-variant association for analysis of pedigree sequence data.Nat Biotechnol. 2014 Jul;32(7):663-9. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2895. Epub 2014 May 18. Nat Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24837662 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Mendelian consistent genotyping errors in pedigrees.Genet Epidemiol. 2014 May;38(4):291-9. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21806. Epub 2014 Apr 9. Genet Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24718985 Free PMC article.
-
Some surprising twists on the road to discovering the contribution of rare variants to complex diseases.Hum Hered. 2012;74(3-4):113-7. doi: 10.1159/000347020. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Hum Hered. 2012. PMID: 23594489 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Elston RC, Stewart J. A general model for the genetic analysis of pedigree data. Human Heredity. 1971;21:523–542. - PubMed
-
- Gusella JF, Wexler NS, Conneally PM, Naylor SL, Anderson MA, Tanzi RE, Watkins PC, Ottina K, Wallace MR, Sakaguchi AY, Young AB, Shoulson I, Bonilla E, Martin JB. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to huntingtons-disease. Nature. 1983;306:234–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 HD055782/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HG005608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG040184/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HD055782/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM046255/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH094400/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH092367/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM046255/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH094293/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG040184/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG040184/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HG005608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094400/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094293/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH092367/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM046255/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

