Meis1 regulates postnatal cardiomyocyte cell cycle arrest
- PMID: 23594737
- PMCID: PMC4159712
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12054
Meis1 regulates postnatal cardiomyocyte cell cycle arrest
Abstract
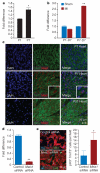
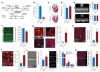
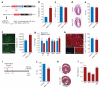
The neonatal mammalian heart is capable of substantial regeneration following injury through cardiomyocyte proliferation. However, this regenerative capacity is lost by postnatal day 7 and the mechanisms of cardiomyocyte cell cycle arrest remain unclear. The homeodomain transcription factor Meis1 is required for normal cardiac development but its role in cardiomyocytes is unknown. Here we identify Meis1 as a critical regulator of the cardiomyocyte cell cycle. Meis1 deletion in mouse cardiomyocytes was sufficient for extension of the postnatal proliferative window of cardiomyocytes, and for re-activation of cardiomyocyte mitosis in the adult heart with no deleterious effect on cardiac function. In contrast, overexpression of Meis1 in cardiomyocytes decreased neonatal myocyte proliferation and inhibited neonatal heart regeneration. Finally, we show that Meis1 is required for transcriptional activation of the synergistic CDK inhibitors p15, p16 and p21. These results identify Meis1 as a critical transcriptional regulator of cardiomyocyte proliferation and a potential therapeutic target for heart regeneration.
Figures

Comment in
-
Regeneration potential of adult cardiac myocytes.Cell Res. 2013 Aug;23(8):978-9. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.78. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23774267 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyocyte cell cycle: Meis-ing something?Cell Cycle. 2014;13(7):1057-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.28379. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24603411 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

