Inhibition of novel β coronavirus replication by a combination of interferon-α2b and ribavirin
- PMID: 23594967
- PMCID: PMC3629412
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01686
Inhibition of novel β coronavirus replication by a combination of interferon-α2b and ribavirin
Abstract
The identification of a novel β coronavirus, nCoV, as the causative agent of severe respiratory illness in humans originating in Saudi Arabia, Qatar and Jordan has raised concerns about the possibility of a coronavirus pandemic similar to that of SARS-CoV. As a definitive treatment regimen has never been thoroughly evaluated for coronavirus infections, there is an urgent need to rapidly identify potential therapeutics to address future cases of nCoV. To determine an intervention strategy, the effect of interferon-α2b and ribavirin on nCoV isolate hCoV-EMC/2012 replication in Vero and LLC-MK2 cells was evaluated. hCoV-EMC/2012 was sensitive to both interferon-α2b and ribavirin alone in Vero and LLC-MK2 cells, but only at relatively high concentrations; however, when combined, lower concentrations of interferon-α2b and ribavirin achieved comparable endpoints. Thus, a combination of interferon-α2b and ribavirin, which are already commonly used in the clinic, may be useful for patient management in the event of future nCoV infections.
Figures

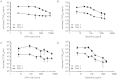
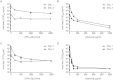
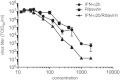
Similar articles
-
Ribavirin and interferon-beta synergistically inhibit SARS-associated coronavirus replication in animal and human cell lines.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Jan 28;326(4):905-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.128. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 15607755 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with interferon-α2b and ribavirin improves outcome in MERS-CoV-infected rhesus macaques.Nat Med. 2013 Oct;19(10):1313-7. doi: 10.1038/nm.3362. Epub 2013 Sep 8. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 24013700 Free PMC article.
-
Human coronavirus EMC does not require the SARS-coronavirus receptor and maintains broad replicative capability in mammalian cell lines.mBio. 2012 Dec 11;3(6):e00515-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00515-12. mBio. 2012. PMID: 23232719 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro inhibition of Chikungunya and Semliki Forest viruses replication by antiviral compounds: synergistic effect of interferon-alpha and ribavirin combination.Antiviral Res. 2004 Feb;61(2):111-7. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2003.09.005. Antiviral Res. 2004. PMID: 14670584
-
Pegylated interferon-α2a and ribavirin versus pegylated interferon-α2b and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C : a meta-analysis.Drugs. 2013 Mar;73(3):263-77. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0027-1. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23436591 Review.
Cited by
-
Where are we with understanding of COVID-19?Adv Biol Regul. 2020 Dec;78:100738. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2020.100738. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Adv Biol Regul. 2020. PMID: 32992235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: current situation and travel-associated concerns.Front Med. 2016 Jun;10(2):111-9. doi: 10.1007/s11684-016-0446-y. Epub 2016 May 4. Front Med. 2016. PMID: 27146399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feasibility of Known RNA Polymerase Inhibitors as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Drugs.Pathogens. 2020 Apr 26;9(5):320. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050320. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32357471 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging novel and antimicrobial-resistant respiratory tract infections: new drug development and therapeutic options.Lancet Infect Dis. 2014 Nov;14(11):1136-1149. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70828-X. Epub 2014 Sep 1. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25189352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on therapeutic options for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV).Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017 Mar;15(3):269-275. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2017.1271712. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017. PMID: 27937060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zaki A. M., van Boheemen S., Bestebroer T. M., Osterhaus A. D. & Fouchier R. A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. The New England journal of medicine 367, 1814–1820 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Buchholz U. et al. Contact investigation of a case of human novel coronavirus infection treated in a German hospital, October-November 2012. Euro surveillance: bulletin europeen sur les maladies transmissibles = European communicable disease bulletin 18, pii = 20406 (2013). - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. . Novel coronavirus infection - update. (2013).<http://www.who.int/csr/don/2013_02_21/en/index.html> [Accessed March 4, 2013].
-
- Wise J. Patient dies from novel coronavirus in UK. BMJ 346, f1133 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

