Identifying differentially expressed genes in pollen from self-incompatible "Wuzishatangju" and self-compatible "Shatangju" mandarins
- PMID: 23595002
- PMCID: PMC3645760
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14048538
Identifying differentially expressed genes in pollen from self-incompatible "Wuzishatangju" and self-compatible "Shatangju" mandarins
Abstract
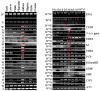
Self-incompatibility (SI) is one of the important factors that can result in seedless fruit in Citrus. However, the molecular mechanism of SI in Citrus is not yet clear. In this study, two suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) libraries (forward, F and reverse, R) were constructed to isolate differentially expressed genes in pollen from "Wuzishatangju" (SI) and "Shatangju" (self-compatibility, SC) mandarins. Four hundred and sixty-eight differentially expressed cDNA clones from 2077 positive clones were sequenced and identified. Differentially expressed ESTs are possibly involved in the SI reaction of "Wuzishatangju" by regulating pollen development, kinase activity, ubiquitin pathway, pollen-pistil interaction, and calcium ion binding. Twenty five SI candidate genes were obtained, six of which displayed specific expression patterns in various organs and stages after self- and cross-pollination. The expression level of the F-box gene (H304) and S1 (F78) in the pollen of "Wuzishatangju" was 5-fold higher than that in "Shatangju" pollen. The F-box gene, S1, UBE2, UBE3, RNaseHII, and PCP were obviously up-regulated in pistils at 3 d after self-pollination of "Wuzishatangju", approximately 3-, 2-, 10-, 5-, 5-, and 2-fold higher, respectively than that at the same stage after cross-pollination of "Wuzishatangju" × "Shatangju" pistils. The potential involvement of these genes in the pollen SI reaction of "Wuzishatangju" is discussed.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes in pistils from self-incompatible Citrus reticulata by suppression subtractive hybridization.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Jan;40(1):159-69. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2045-6. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23070907
-
Molecular characterization and expression analysis of S1 self-incompatibility locus-linked pollen 3.15 gene in Citrus reticulata.J Integr Plant Biol. 2013 May;55(5):443-52. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12026. Epub 2013 Apr 3. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23302024
-
Cloning and expression analysis of S-RNase homologous gene in Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Wuzishatangju.Plant Sci. 2011 Feb;180(2):358-67. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.10.012. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Plant Sci. 2011. PMID: 21421381
-
Robust self-incompatibility in the absence of a functional ARC1 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell. 2014 Oct;26(10):3838-41. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.129387. Epub 2014 Oct 21. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25336507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming self-incompatibility in grasses: a pathway to hybrid breeding.Theor Appl Genet. 2016 Oct;129(10):1815-29. doi: 10.1007/s00122-016-2775-2. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Theor Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 27577253 Review.
Cited by
-
Reproduction in woody perennial Citrus: an update on nucellar embryony and self-incompatibility.Plant Reprod. 2018 Mar;31(1):43-57. doi: 10.1007/s00497-018-0327-4. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Plant Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29457194 Review.
-
Evolution of self-compatibility by a mutant Sm-RNase in citrus.Nat Plants. 2020 Feb;6(2):131-142. doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0597-3. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Nat Plants. 2020. PMID: 32055045 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative studies of mitochondrial proteomics reveal an intimate protein network of male sterility in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).J Exp Bot. 2015 Oct;66(20):6191-203. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv322. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 26136264 Free PMC article.
-
CrWSKP1, an SKP1-like Gene, Is Involved in the Self-Incompatibility Reaction of "Wuzishatangju" (Citrus reticulata Blanco).Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 9;16(9):21695-710. doi: 10.3390/ijms160921695. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26370985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Nettancourt D. Incompatibility in angiosperms. Sex Plant Reprod. 1997;10:185–199.
-
- Takayama S., Shimosato H., Shiba H., Funato M., Che F.S., Watanabe M., Iwano M., Isogai A. Direct ligand-receptor complex interaction controls Brassica self-incompatibility. Nature. 2001;413:534–538. - PubMed
-
- Lai Z., Ma W., Han B., Liang L., Zhang Y., Hong G., Xue Y. An F-box gene linked to the self-incompatibility (S) locus of Antirrhinum is expressed specifically in pollen and tapetum. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002;50:29–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

