Cerebellar learning distinguishes inflammatory neuropathy with and without tremor
- PMID: 23596070
- PMCID: PMC3908356
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318292a2b8
Cerebellar learning distinguishes inflammatory neuropathy with and without tremor
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to investigate if patients with inflammatory neuropathies and tremor have evidence of dysfunction in the cerebellum and interactions in sensorimotor cortex compared to nontremulous patients and healthy controls.
Methods: A prospective data collection study investigating patients with inflammatory neuropathy and tremor, patients with inflammatory neuropathy without tremor, and healthy controls on a test of cerebellar associative learning (eyeblink classical conditioning), a test of sensorimotor integration (short afferent inhibition), and a test of associative plasticity (paired associative stimulation). We also recorded tremor in the arms using accelerometry and surface EMG.
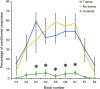
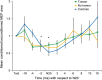
Results: We found impaired responses to eyeblink classical conditioning and paired associative stimulation in patients with neuropathy and tremor compared with neuropathy patients without tremor and healthy controls. Short afferent inhibition was normal in all groups.
Conclusions: Our data strongly suggest impairment of cerebellar function is linked to the production of tremor in patients with inflammatory neuropathy.
Figures

References
-
- Lunn MP, Willison HJ. Diagnosis and treatment in inflammatory neuropathies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009;80:249–258 - PubMed
-
- Smith IS, Kahn SN, Lacey BW, et al. Chronic demyelinating neuropathy associated with benign IgM paraproteinaemia. Brain 1983;106:169–195 - PubMed
-
- Smith IS. The natural history of chronic demyelinating neuropathy associated with benign IgM paraproteinaemia: a clinical and neurophysiological study. Brain 1994;117:949–957 - PubMed
-
- Saifee TA, Schwingenschuh P, Reilly MM, et al. Tremor in inflammatory neuropathies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. Epub 2012 Sept 5 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
