Effects of early chemotherapeutic treatment on learning in adolescent mice: implications for cognitive impairment and remediation in childhood cancer survivors
- PMID: 23596103
- PMCID: PMC3674165
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3764
Effects of early chemotherapeutic treatment on learning in adolescent mice: implications for cognitive impairment and remediation in childhood cancer survivors
Abstract
Purpose: Among children diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and given chemotherapy-only treatment, 40% to 70% of survivors experience neurocognitive impairment. The present study used a preclinical mouse model to investigate the effects of early exposure to common ALL chemotherapeutics methotrexate (MTX) and cytarabine (Ara-C) on learning and memory.
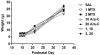
Experimental design: Preweanling mouse pups were treated on postnatal day (PND) 14, 15, and 16 with saline, MTX, Ara-C, or a combination of MTX and Ara-C. Nineteen days after treatment (PND 35), behavioral tasks measuring different aspects of learning and memory were administered.
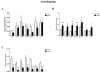
Results: Significant impairment in acquisition and retention over both short (1 hour) and long (24 hours) intervals, as measured by autoshaping and novel object recognition tasks, was found following treatment with MTX and Ara-C. Similarly, a novel conditional discrimination task revealed impairment in acquisition for chemotherapy-treated mice. No significant group differences were found following the extensive training component of this task, with impairment following the rapid training component occurring only for the highest MTX and Ara-C combination group.
Conclusions: Findings are consistent with those from clinical studies suggesting that childhood cancer survivors are slower at learning new information and primarily exhibit deficits in memory years after successful completion of chemotherapy. The occurrence of mild deficits on a novel conditional discrimination task suggests that chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment may be ameliorated through extensive training or practice.
©2013 AACR
Figures
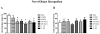
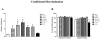
References
-
- Pui C, Evans WE. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:166–178. - PubMed
-
- Spiegler BJ, Kennedy K, Maze R, Greenberg ML, Weitzman S, Hitzler JK, et al. Comparison of long-term neurocognitive outcomes in young children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with cranial radiation or high-dose or very high-dose intravenous methotrexate. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(24):3858–3864. - PubMed
-
- Waber DP, Turek J, Catania L, Stevenson K, Robaey P, Romero I, et al. Neuropsychological outcomes from a randomized trial of triple intrathecal chemotherapy compared with 18 gy cranial radiation as CNS treatment in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: findings from Dana-Farber cancer institute ALL consortium protocol 95-01. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4914–4921. - PubMed
-
- Krull KR, Okcu MF, Potter B, Jain N, Dreyer Z, Kamdar K, et al. Screening for neurocognitive impairment in pediatric cancer long-term survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(25):4138–4143. - PubMed
-
- Buizer AI, de Sonneville LMJ, Veerman AJP. Effects of chemotherapy on neurocognitive function in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a critical review of the literature. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;52:447–454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

