Intraduct papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: a tumour linked with IgG4-related disease?
- PMID: 23596150
- PMCID: PMC3850253
- DOI: 10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201516
Intraduct papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: a tumour linked with IgG4-related disease?
Abstract
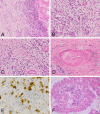
Objectives: Intraduct papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a pancreatic tumour that is often associated with chronic pancreatitis (CP) in the surrounding pancreas. Type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is a fibro-inflammatory condition with characteristic histological features and prominent IgG4+ plasma cells and is part of the spectrum of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). The aim of this study was to determine whether CP associated with pancreatic IPMN commonly represents AIP.
Methods: We identified two consecutive 'index' cases of pancreatic IPMN during routine reporting in which the adjacent pancreas showed morphological features suggestive of AIP. These cases were investigated using the Boston criteria for the histopathological diagnosis of IgG4-RD and the HISORt criteria for the clinical and histopathological diagnosis of AIP. Using the same criteria, we proceeded to a clinical review of 12 extra cases of IPMN in which the tumour or the surrounding pancreas showed significant lymphoplasmacytic inflammation and/or fibrosis.
Results: Both of the 'index' cases fulfilled the HISORt criteria for AIP and both had morphological features characteristic of IgG4-RD using the Boston criteria, although only one possessed features 'highly suggestive of IgG4-RD' after immunohistochemistry. Additionally, both 'index' cases had radiological features that could represent extrapancreatic manifestations. Review of the 12 additional cases of IPMN revealed no further examples showing co-existent AIP.
Conclusion: While pancreatic IPMN and AIP may co-exist, most CP associated with IPMN does not represent AIP.
Keywords: INFLAMMATION; PANCREAS; PANCREATIC CANCER.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas and IgG4-related disease: a coincidental association.Pancreatology. 2013 Jul-Aug;13(4):379-83. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2013.04.197. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Pancreatology. 2013. PMID: 23890136
-
Association of IgG4 response and autoimmune pancreatitis with intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms.Pancreatology. 2017 Mar-Apr;17(2):263-266. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Pancreatology. 2017. PMID: 28215485
-
Autoimmune pancreatitis type-1 associated with intraduct papillary mucinous neoplasm: report of two cases.Pancreatology. 2014 Jul-Aug;14(4):316-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2014.04.032. Epub 2014 May 9. Pancreatology. 2014. PMID: 25062884
-
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: reporting clinically relevant features.Histopathology. 2017 May;70(6):850-860. doi: 10.1111/his.13131. Epub 2017 Jan 15. Histopathology. 2017. PMID: 27878841 Review.
-
Diagnosis and classification of autoimmune pancreatitis.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Apr-May;13(4-5):451-8. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 12. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 24424184 Review.
Cited by
-
A Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas Associated With IgG4-Related Pancreatitis: A Case Report.Int J Surg Pathol. 2017 May;25(3):271-275. doi: 10.1177/1066896916677289. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Int J Surg Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28107092 Free PMC article.
-
Histological features of autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with a correlation with imaging findings.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2021 Oct;48(4):581-594. doi: 10.1007/s10396-021-01148-5. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2021. PMID: 34669070 Review.
-
European Guideline on IgG4-related digestive disease - UEG and SGF evidence-based recommendations.United European Gastroenterol J. 2020 Jul;8(6):637-666. doi: 10.1177/2050640620934911. Epub 2020 Jun 18. United European Gastroenterol J. 2020. PMID: 32552502 Free PMC article.
-
Multilocular Cyst of Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis Masquerading as Cancerization of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm.Intern Med. 2020 Jan 15;59(2):199-204. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3561-19. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 31484912 Free PMC article.
-
Coexisting Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Mixed-type Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm.Intern Med. 2021 Sep 1;60(17):2793-2797. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.6514-20. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33746160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Culver EL, Bateman AC. General principles of IgG4-related disease. Diagn Histopathol 2013;19:111–18.
-
- Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ, et al. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: the Mayo Clinic experience. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4:1010–16. - PubMed
-
- Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan J, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol 2012;25:1181–92. - PubMed
-
- Strehl J, Hartmann A, Agaimy A. Numerous IgG4-positive plasma cells are ubiquitous in diverse localised non-specific inflammatory conditions and need to be distinguished from IgG4-related systemic disorders. J Clin Pathol 2011;64:237–43. - PubMed
-
- Deheragoda MG, Church NI, Rodriguez-Justo M, et al. The use of immunoglobulin G4 immunostaining in diagnosing pancreatic and extrapancreatic involvement in autoimmune pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:1229–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
