Simultaneous neutralization and innate immune detection of a replicating virus by TRIM21
- PMID: 23596308
- PMCID: PMC3700317
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00647-13
Simultaneous neutralization and innate immune detection of a replicating virus by TRIM21
Abstract
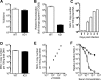
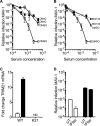
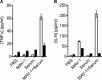
Tripartite motif-containing 21 (TRIM21) is a cytosolic immunoglobulin receptor that mediates antibody-dependent intracellular neutralization (ADIN). Here we show that TRIM21 potently inhibits the spreading infection of a replicating cytopathic virus and activates innate immunity. We used a quantitative PCR (qPCR)-based assay to measure in vitro replication of mouse adenovirus type 1 (MAV-1), a virus that causes dose-dependent hemorrhagic encephalitis in mice. Using this assay, we show that genetic ablation of TRIM21 or chemical inhibition of either the AAA ATPase p97/valosin-containing protein (VCP) or the proteasome results in a >1,000-fold increase in the relative level of infection in the presence of immune serum. Moreover, the TRIM21-mediated ability of antisera to block replication was a consistent feature of the humoral immune response in immunized mice. In the presence of immune sera and upon infection, TRIM21 also activates a proinflammatory response, resulting in secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These results demonstrate that TRIM21 provides a potent block to spreading infection and induces an antiviral state.
Figures
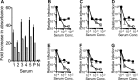
References
-
- Male D, Brostoff J, Roth D, Roitt I. (ed). 2006. Immunology, 17th ed Mosby/Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

