Usefulness of a selective neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, in acute lung injury patients with sepsis
- PMID: 23596346
- PMCID: PMC3627345
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S42004
Usefulness of a selective neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, in acute lung injury patients with sepsis
Abstract
Background: Neutrophil elastase plays a crucial role in the development of acute lung injury (ALI) in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). The clinical efficacy of the neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, for patients with ALI associated with SIRS has not been convincingly demonstrated. The aim of this study was to determine if there are clinical features of patients with this condition that affect the efficacy of sivelestat.
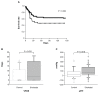
Methods: This was a retrospective study of 110 ALI patients with SIRS. Clinical information, including the etiology of ALI, the number of organs failing, scoring systems for assessing the severity of illness, and laboratory data, was collected at the time of diagnosis. Information on the number of ventilator-free days (VFDs) and changes in PaO(2)/F(I)O(2) (ΔP/F) before and 7 days after the time of ALI diagnosis was also collected. The effect of sivelestat on ALI patients was also examined based on whether they had sepsis and whether their initial serum procalcitonin level was ≥0.5 ng/mL.
Results: There were 70 patients who were treated with sivelestat and 40 control patients. VFDs and ΔP/F were significantly higher in the treated patients than in the control patients. However, there was no significant difference in the patient survival rate between the two groups. Sivelestat was more effective in ALI patients with a PaO(2)/F(I)O(2) ratio ≥ 140 mmHg or sepsis. Sivelestat significantly prolonged survival and led to higher VFDs and increased ΔP/F in septic patients and patients with initial serum procalcitonin levels ≥ 0.5 ng/mL.
Conclusion: The results may facilitate a future randomized controlled trial to determine whether sivelestat is beneficial for ALI patients with sepsis.
Keywords: neutrophil elastase; procalcitonin; systemic inflammatory response syndrome; ventilator-free days.
Figures



References
-
- Aikawa N, Ishizaka A, Hirasawa H, et al. Reevaluation of the efficacy and safety of the neutrophil elastase inhibitor, Sivelestat, for the treatment of acute lung injury associated with systemic inflammatory response syndrome; a phase IV study. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2011;24(5):549–554. - PubMed
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(18):1334–1349. - PubMed
-
- Weiland JE, Davis WB, Holter JF, Mohammed JR, Dorinsky PM, Gadek JE. Lung neutrophils in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clinical and pathophysiologic significance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;133(2):218–225. - PubMed
-
- Idell S, Kucich U, Fein A, et al. Neutrophil elastase-releasing factors in bronchoalveolar lavage from patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;132(5):1098–1105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

