Economic evaluation of therapies for patients suffering from relapsed-refractory multiple myeloma in Greece
- PMID: 23596356
- PMCID: PMC3627436
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S43373
Economic evaluation of therapies for patients suffering from relapsed-refractory multiple myeloma in Greece
Abstract
Background: Multiple myeloma is a hematologic malignancy that incurs a substantial economic burden in care management. Since most patients with multiple myeloma eventually relapse or become refractory to current therapies (rrMM), the aim of this study was to assess the cost-effectiveness of the combination of lenalidomide-dexamethasone, relative to bortezomib alone, in patients suffering from rrMM in Greece.
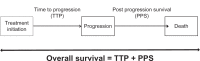
Methods: An international discrete event simulation model was locally adapted to estimate differences in overall survival and treatment costs associated with the two alternative treatment options. The efficacy data utilized came from three international trials (MM-009, MM-010, APEX). Quality of life data were extracted from the published literature. Data on resource use and prices came from relevant local sources and referred to 2012. The perspective of the analysis was that of public providers. Total costs for monitoring and administration of therapy to patients, management of adverse events, and cost of medication were captured. A 3.5% discount rate was used for costs and health outcomes. A Monte Carlo simulation was used to estimate probabilistic results with 95% uncertainty intervals (UI) and a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve.
Results: The mean number of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) was 3.01 (95% UI 2.81-3.20) and 2.22 (95% UI 2.02-2.41) for lenalidomide-dexamethasone and bortezomib, respectively, giving an incremental gain of 0.79 (95% UI 0.49-1.06) QALYs in favor of lenalidomide-dexamethasone. The mean cost of therapy per patient was estimated at €80;77,670 (95% UI €80;76,509-€80;78,900) and €80;48,928 (95% UI €80;48,300-€80;49,556) for lenalidomide-dexamethasone and bortezomib, respectively. The incremental cost per life year gained with lenalidomide-dexamethasone was estimated at €80;29,415 (95% UI €80;23,484-€80;37,583) and the incremental cost per QALY gained at €80;38,268 (95% UI €80;27,001-€80;58,065). The probability of lenalidomide-dexamethasone being a cost-effective therapy option at a threshold three times the per capita income (€80;60,000 per QALY) was higher than 95%. The results remained constant, without altering the conclusions, under several hypothetical scenarios.
Conclusion: The combination of lenalidomide and dexamethasone may represent a cost-effective choice relative to bortezomib monotherapy for patients in Greece with previously treated multiple myeloma.
Keywords: bortezomib; dexamethasone; economic evaluation; lenalidomide; multiple myeloma.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Globocan. Country Fast Stats 2008Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr/factsheets/populations/factsheet.asp?uno=968Accessed September 12, 2012
-
- Becker N. Epidemiology of multiple myeloma. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011;183:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig H, Bolejack V, Crowley J, et al. Survival and years of life lost in different age cohorts of patients with multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1599–1605. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

