Hippocampus-dependent learning influences hippocampal neurogenesis
- PMID: 23596385
- PMCID: PMC3627134
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00057
Hippocampus-dependent learning influences hippocampal neurogenesis
Abstract
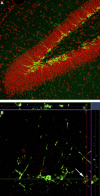
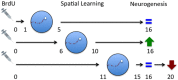
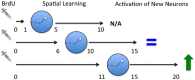
The structure of the mammalian hippocampus continues to be modified throughout life by continuous addition of neurons in the dentate gyrus. Although the existence of adult neurogenesis is now widely accepted the function that adult generated granule cells play is a topic of intense debate. Many studies have argued that adult generated neurons, due to unique physiological characteristics, play a unique role in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory. However, it is not currently clear whether this is the case or what specific capability adult generated neurons may confer that developmentally generated neurons do not. These questions have been addressed in numerous ways, from examining the effects of increasing or decreasing neurogenesis to computational modeling. One particular area of research has examined the effects of hippocampus dependent learning on proliferation, survival, integration and activation of immature neurons in response to memory retrieval. Within this subfield there remains a range of data showing that hippocampus dependent learning may increase, decrease or alternatively may not alter these components of neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Determining how and when hippocampus-dependent learning alters adult neurogenesis will help to further clarify the role of adult generated neurons. There are many variables (such as age of immature neurons, species, strain, sex, stress, task difficulty, and type of learning) as well as numerous methodological differences (such as marker type, quantification techniques, apparatus size etc.) that could all be crucial for a clear understanding of the interaction between learning and neurogenesis. Here, we review these findings and discuss the different conditions under which hippocampus-dependent learning impacts adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus.
Keywords: cell survival; dentate gyrus; hippocampus; memory; neurogenesis; spatial learning.
Figures
References
-
- Altman J., Das G. D. (1965). Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 124, 319–335 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

