Transcranial direct-current stimulation increases extracellular dopamine levels in the rat striatum
- PMID: 23596399
- PMCID: PMC3622879
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsys.2013.00006
Transcranial direct-current stimulation increases extracellular dopamine levels in the rat striatum
Abstract
Background: Transcranial direct-current stimulation (tDCS) is a non-invasive procedure that achieves polarity-dependent modulation of neuronal membrane potentials. It has recently been used as a functional intervention technique for the treatment of psychiatric and neurological diseases; however, its neuronal mechanisms have not been fully investigated in vivo.
Objective/hypothesis: To investigate whether the application of cathodal or anodal tDCS affects extracellular dopamine and serotonin levels in the rat striatum.
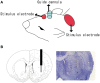
Methods: Stimulation and in vivo microdialysis were carried out under urethane anesthesia, and microdialysis probes were slowly inserted into the striatum. After the collection of baseline fractions in the rat striatum, cathodal or anodal tDCS was applied continuously for 10 min with a current intensity of 800 μA from an electrode placed on the skin of the scalp. Dialysis samples were collected every 10 min until at least 400 min after the onset of stimulation.
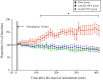
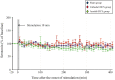
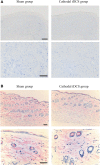
Results: Following the application of cathodal, but not anodal, tDCS for 10 min, extracellular dopamine levels increased for more than 400 min in the striatum. There were no significant changes in extracellular serotonin levels.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that tDCS has a direct and/or indirect effect on the dopaminergic system in the rat basal ganglia.
Keywords: Parkinson disease; basal ganglia; dopamine; striatum; transcranial direct current stimulation.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander G. E., Crutcher M. D. (1990). Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 13, 266–271 - PubMed
-
- Bachmann C. G., Muschinsky S., Nitsche M. A., Rolke R., Magerl W., Treede R. D., et al. (2010). Transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor cortex induces distinct changes in thermal and mechanical sensory percepts. Clin. Neurophysiol. 121, 2083–2089 10.1016/j.clinph.2010.05.005 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

