Dopaminergic basis of the psychosis-prone personality investigated with functional magnetic resonance imaging of procedural learning
- PMID: 23596404
- PMCID: PMC3626071
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00130
Dopaminergic basis of the psychosis-prone personality investigated with functional magnetic resonance imaging of procedural learning
Abstract
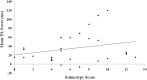
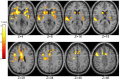
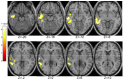
Previous evidence shows a reliable association between psychosis-prone (especially schizotypal) personality traits and performance on dopamine (DA)-sensitive tasks (e.g., prepulse inhibition and antisaccade). Here, we used blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) fMRI and an established procedural learning (PL) task to examine the dopaminergic basis of two aspects of psychosis-proneness (specific schizotypy and general psychoticism). Thirty healthy participants (final N = 26) underwent fMRI during a blocked, periodic sequence-learning task which, in previous studies, has been shown to reveal impaired performance in schizophrenia patients given drugs blocking the DA D2 receptor subtype (DRD2), and to correspond with manipulation of DA activity and elicit fronto-striatal-cerebellar activity in healthy people. Psychosis-proneness was indexed by the Psychoticism (P) scale of the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire-Revised (EPQ-R; 1991) and the Schizotypal Personality Scale (STA; 1984). EPQ-R Extraversion and Neuroticism scores were also examined to establish discriminant validity. We found a positive correlation between the two psychosis-proneness measures (r = 0.43), and a robust and unique positive association between EPQ-R P and BOLD signal in the putamen, caudate, thalamus, insula, and frontal regions. STA schizotypy score correlated positively with activity in the right middle temporal gyrus. As DA is a key transmitter in the basal ganglia, and the thalamus contains the highest levels of DRD2 receptors of all extrastriatal regions, our results support a dopaminergic basis of psychosis-proneness as measured by the EPQ-R Psychoticism.
Keywords: dopamine; schizotypy; sequence learning; striatum; thalamus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prepulse inhibition and "psychosis-proneness" in healthy individuals: an fMRI study.Eur Psychiatry. 2008 Jun;23(4):274-80. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.11.006. Epub 2008 Jan 25. Eur Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18222069
-
Correlation of individual differences in schizotypal personality traits with amphetamine-induced dopamine release in striatal and extrastriatal brain regions.Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Apr;168(4):418-26. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10020165. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Am J Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21159728 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Striatal dopamine (D2) receptor availability predicts socially desirable responding.Neuroimage. 2007 Feb 15;34(4):1782-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.10.042. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Neuroimage. 2007. PMID: 17188897
-
[Cognition, schizophrenia and the effect of antipsychotics].Encephale. 2006 May-Jun;32(3 Pt 1):341-50. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(06)76162-0. Encephale. 2006. PMID: 16840928 Review. French.
-
Inhibitory deficits in prepulse inhibition, sensory gating, and antisaccade eye movement in schizotypy.Int J Psychophysiol. 2017 Apr;114:47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Int J Psychophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28189549 Review.
Cited by
-
A potential link between gambling addiction severity and central dopamine levels: Evidence from spontaneous eye blink rates.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 6;8(1):13371. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31531-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30190487 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics, cognition, and neurobiology of schizotypal personality: a review of the overlap with schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2014 Feb 21;5:18. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00018. eCollection 2014. Front Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24600411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of schizotypy with striatocortical functional connectivity and its asymmetry in healthy adults.Hum Brain Mapp. 2018 Jan;39(1):288-299. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23842. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018. PMID: 29024192 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Processes and Resting-State Functional Neuroimaging Findings in High Schizotypal Individuals and Schizotypal Personality Disorder Patients: A Systematic Review.Brain Sci. 2023 Apr 4;13(4):615. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13040615. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37190580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common and distinct neural effects of risperidone and olanzapine during procedural learning in schizophrenia: a randomised longitudinal fMRI study.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Sep;232(17):3135-47. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3959-1. Epub 2015 May 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25980483 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Alexander G. E., Crutcher M. D. (1990). Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 13, 266–271 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

