Protective effects of Radix Pseudostellariae polysaccharides against exercise-induced oxidative stress in male rats
- PMID: 23596474
- PMCID: PMC3628077
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2013.942
Protective effects of Radix Pseudostellariae polysaccharides against exercise-induced oxidative stress in male rats
Abstract
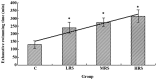
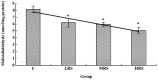
The main purpose of this study was to examine the effect of Radix Pseudostellariae polysaccharides (RPPs) against swimming exercise-induced oxidative stress in male rats. A total of 40 male Wistar rats were randomized into four groups: the control (C), low-dose RPP supplementation (LRS), medium-dose RPP supplementation (MRS) and high-dose RPP supplementation (HRS) groups. The control group received saline solution and the supplementation groups received different doses of RPPs (100, 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight, respectively). The animals were medicated orally and daily for 28 days. On day 28, the rats were made to swim until exhausted. The exhaustive swimming time and various biochemical parameters, including blood lactate, hemoglobin, catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and malondialdehyde (MDA), were measured. The results showed that RPP supplementation elevates the exercise tolerance and decreases the blood lactate level of rats following exhaustive swimming exercise. RPP supplementation augments the levels of hemoglobin and anti-oxidant enzymes (CAT, SOD and GSH-Px), and effectively decreases the MDA content of the skeletal muscle of rats, which suggests that RPP supplementation has a protective effect against exercise-induced oxidative stress.
Keywords: Radix Pseudostellariae polysaccharides; oxidative stress; rats; swimming exercise.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides supplementation attenuates exercise-induced oxidative stress in skeletal muscle of mice.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2014 Apr;21(2):119-23. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24600303 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CoQ10 supplementation and swimming training on exhaustive exercise-induced oxidative stress in rat heart.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2012;113(7):393-9. doi: 10.4149/bll_2012_089. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2012. PMID: 22794511
-
Polysaccharides from Cordyceps sinensis mycelium ameliorate exhaustive swimming exercise-induced oxidative stress.Pharm Biol. 2014 Feb;52(2):157-61. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2013.820197. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Pharm Biol. 2014. PMID: 24047103
-
Effects of Laminaria japonica polysaccharides on exercise endurance and oxidative stress in forced swimming mouse model.J Biol Res (Thessalon). 2016 Apr 26;23:7. doi: 10.1186/s40709-016-0049-4. eCollection 2016 Dec. J Biol Res (Thessalon). 2016. PMID: 27119074 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of L-arginine on pulmonary oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses during exhaustive exercise in rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005 Aug;26(8):992-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00155.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005. PMID: 16038634
Cited by
-
Penehyclidine Hydrochloride Preconditioning Provides Cardioprotection in a Rat Model of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 2;10(12):e0138051. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138051. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26632817 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-Induced Regulation of Redox Status in Cardiovascular Diseases: The Role of Exercise Training and Detraining.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Dec 23;9(1):13. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010013. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31877965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Short Overview of Changes in Inflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress in Response to Physical Activity and Antioxidant Supplementation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Sep 18;9(9):886. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090886. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32962110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antifatigue Effect of Luteolin-6-C-Neohesperidoside on Oxidative Stress Injury Induced by Forced Swimming of Rats through Modulation of Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathways.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3159358. doi: 10.1155/2017/3159358. Epub 2017 May 15. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28588747 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of polysaccharides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.), Makino on physical fatigue.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014 Apr 3;11(3):112-7. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v11i3.17. eCollection 2014. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25371572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessio HM. Exercise-induced oxidative stress. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993;25:218–224. - PubMed
-
- Bejma J, Ji LL. Aging and acute exercise enhance free radical generation in rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 1999;87:465–470. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar M, Pillai KK, Vohora D. Effect of thioperamide on modified forced swimming test-induced oxidative stress in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;97:218–221. - PubMed
-
- Pepe H, Balci SS, Revan S, Akalin PP, Kurtoğlu F. Comparison of oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity before and after running exercises in both sexes. Gend Med. 2009;6:587–595. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee AK, Mandal A, Chanda D, Chakraborti S. Oxidant, antioxidant and physical exercise. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;253:307–312. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
