Clinical study on the application of a 2- μ m continuous wave laser in transurethral vaporesection of the prostate
- PMID: 23596476
- PMCID: PMC3628398
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2013.951
Clinical study on the application of a 2- μ m continuous wave laser in transurethral vaporesection of the prostate
Abstract
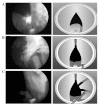
The present study aimed to evaluate the method and clinical effects of transurethral dividing vaporesection of the prostate in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) using the RevoIix 70 W 2-μm continuous wave (cw) laser. A total of 155 BPH patients were treated transurethrally under epidural or sacral anesthesia using the dividing vaporesection technique. Of these, 80 had a prostate volume of ≤80 ml and 75 had a prostate volume of >80 ml. Pre- and post-operative data were evaluated for prostate-specific antigens (PSAs), post-void residual volume (PVR), maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and quality of life (QoL). Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 16.0 software. Treatment effectiveness evaluations were also conducted. In the ≤80 ml prostate volume group, the mean PSA level decreased from 3.8±0.9 to 2.6±1.3 ng/ml. The PVR, mean Qmax, IPSS and QoL score improved significantly (P<0.05) in each group but no statistically significant difference was identified between the two groups. With a shorter surgery duration, safe use and high cutting efficiency and rapid vaporization ability, the 2-μm laser vaporesection technique shows superiority compared to standard techniques in the treatment of BPH.
Keywords: 2-μm continuous wave laser; benign prostatic hyperplasia; transurethral resection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[5-year follow-up to transurethral vaporesection of the prostate using the 2 micron continuous wave laser for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Feb 1;51(2):119-22. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23711003 Chinese.
-
Vaporesection for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia using a 2-microm continuous-wave laser: a prospective trial with 1-year follow-up.BJU Int. 2009 Feb;103(3):352-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08040.x. Epub 2008 Sep 3. BJU Int. 2009. PMID: 18778340 Clinical Trial.
-
Application of two micron laser vaporesection combined with transurethral resection of the prostate in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: analysis of 340 cases.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Oct 15;8(10):19418-23. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26770585 Free PMC article.
-
Thulium laser VapoResection of the prostate versus traditional transurethral resection of the prostate or transurethral plasmakinetic resection of prostate for benign prostatic obstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Urol. 2018 Sep;36(9):1355-1364. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2287-6. Epub 2018 Apr 12. World J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29651642
-
Safety and Efficacy of Thulium Laser Prostatectomy Versus Transurethral Resection of Prostate for Treatment of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia: A Meta-Analysis.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2016 Sep;8(3):165-70. doi: 10.1111/luts.12092. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2016. PMID: 27619781 Review.
Cited by
-
Re-epithelialization resulted from prostate basal cells in canine prostatic urethra may represent the ideal healing method after two-micron laser resection of the prostate.Asian J Androl. 2015 Sep-Oct;17(5):831-8. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.146972. Asian J Androl. 2015. PMID: 25652631 Free PMC article.
-
One day surgery in the treatment of benign prostatic enlargement with thulium laser: A single institution experience.Korean J Urol. 2015 May;56(5):365-9. doi: 10.4111/kju.2015.56.5.365. Epub 2015 May 4. Korean J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25964837 Free PMC article.
-
Urine can speed up the re-epithelialization process of prostatic urethra wounds by promoting the proliferation and migration of prostate epithelial cells.Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Jan;51(1):9-15. doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-2019-2. Epub 2018 Nov 7. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30402718 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analytical model for CW laser induced heat in turbid media.Opt Express. 2015 Nov 30;23(24):31069-84. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.031069. Opt Express. 2015. PMID: 26698736 Free PMC article.
-
Are Histological Findings of Thulium Laser Vapo-Enucleation Versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Comparable?Pathol Oncol Res. 2015 Sep;21(4):1071-5. doi: 10.1007/s12253-015-9931-x. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Pathol Oncol Res. 2015. PMID: 25862670
References
-
- Wu SL, Li NC, Xiao YX, et al. Natural history of benign prostate hyperplasia. Chin Med J (Engl) 2006;119:2085–2089. - PubMed
-
- Roehrborn CG, Issa MM, Bruskewitz RC, et al. Transurethral needle ablation for benign prostatic hyperplasia: 12-month results of a prospective, multicenter U.S. study. Urology. 1998;51:415–421. - PubMed
-
- de la Rosette JJ, de Wildt MJ, Alivizatos G, Froeling FM, Debruyne FM. Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) in benign prostatic hyperplasia: placebo versus TUMT. Urology. 1994;44:58–63. - PubMed
-
- Madersbacher S, Alivizatos G, Nordling J, Sanz CR, Emberton M, de la Rosette JJ. EAU 2004 guidelines on assessment, therapy and follow-up of men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction (BPH guidelines) Eur Urol. 2004;46:547–554. - PubMed
-
- Gupta N, Sivaramakrishna, Kumar R, Dogra PN, Seth A. Comparison of standard transurethral resection, transurethral vapour resection and holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia of >40 g. BJU Int. 2006;97:85–89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
