The prevention, diagnosis and treatment of premature labor
- PMID: 23596503
- PMCID: PMC3627164
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0227
The prevention, diagnosis and treatment of premature labor
Abstract
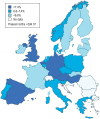
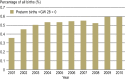
Background: The percentage of preterm births in Germany is high at 9%, but stable. 77% of cases of perinatal death are in prematurely born infants. Intensive research efforts are being directed toward the development of new means of primary and secondary prevention, diagnostic assessment, and pharmacotherapy of premature labor.
Methods: We review pertinent publications that were retrieved by a selective search of the literature from 1966 to 2012, including current meta-analyses from the Cochrane database and the guidelines of German and foreign obstetric societies.
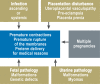
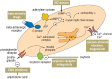
Results: Preterm labor is a multifactorial problem. The current treatment options are symptomatic, rather than causally directed. Preventive treatment with progesterone can lower the rate of preterm birth in high-risk groups by more than 30%. Transporting the pregnant women to an appropriately qualified perinatal care center and induction of fetal lung maturation lowers perinatal mortality. A variety of tocolytic drugs with different mechanisms of action (betamimetics, oxytocin antagonists, calcium-channel blockers, NO donors, and inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis) can be used for individualized tocolytic treatment. Premature rupture of the membranes is an indication for antibiotics.
Conclusion: The goal of all attempts to prevent and treat preterm labor is to improve preterm infants' chances of surviving with as few complications as possible. The methods discussed here can be used to prolong pregnancies at risk for preterm labor and so to reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality.
Figures
Comment in
-
Correspondence (letter to the editor): Numerous errors.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Aug;110(33-34):557. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0557a. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24069080 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correspondence (letter to the editor): Primary prevention of premature labor was given short shrift.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Aug;110(33-34):557-8. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0557b. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24069081 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correspondence (letter to the editor): thyroid function as a possible cause.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Aug;110(33-34):558. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0558a. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24069082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correspondence (letter to the editor): Administration of vitamin D.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Aug;110(33-34):558-9. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0558b. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24069083 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correspondence (letter to the editor): Previous induced terminations.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Aug;110(33-34):559. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0559a. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24069084 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correspondence (letter to the editor): The coagulation status should be determined.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Aug;110(33-34):559. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0559b. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24069085 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correspondence (reply): In reply.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Aug;110(33-34):560. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0560. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24069086 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Gynäkologie und Geburtshilfe Leitlinie 015/025 Medikamentöse Wehenhemmung bei drohender Frühgeburt. www.agmfm.de/_download/unprotected/g_04_03_01_medikamentoese_wehenhemmun....
-
- AQUA - Institut für angewandte Qualitätsförderung und Forschung im Gesundheitswesen GmbH. Bundesauswertung zum Verfahrensjahr 2010 16/1 - Geburtshilfe. www.sqg.de/ergebnisse/leistungsbereiche/geburtshilfe.html.
-
- EURO-PERISTAT Project. European Perinatal Health Report 2008. www.europeristat.com/our-publications/european-perinatal-health-report.html.
-
- Dudenhausen JW, Friese K, Kirschner W. Präkonzeptionelle Gesundheitsberatung und Beratung zur Wahl der Geburtsklinik als weitere Instrumente zur Verringerung von Frühgeburten. Z Geburtsh Neonatol. 2007;211:142–146. - PubMed
-
- RCOG Green-top Guideline No. 1b, February 2011. Tocolysis for women in preterm labour. www.rcog.org.uk/files/rcog-corp/GTG1b26072011.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

