The C-type lectin of the aggrecan G3 domain activates complement
- PMID: 23596522
- PMCID: PMC3626604
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061407
The C-type lectin of the aggrecan G3 domain activates complement
Abstract
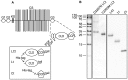
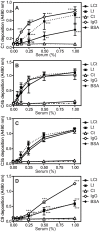
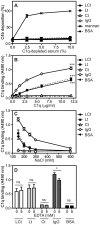
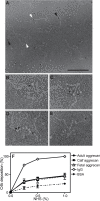
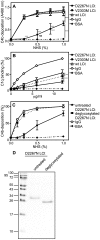
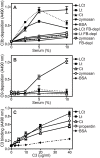
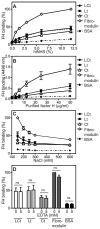
Excessive complement activation contributes to joint diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis during which cartilage proteins are fragmented and released into the synovial fluid. Some of these proteins and fragments activate complement, which may sustain inflammation. The G3 domain of large cartilage proteoglycan aggrecan interacts with other extracellular matrix proteins, fibulins and tenascins, via its C-type lectin domain (CLD) and has important functions in matrix organization. Fragments containing G3 domain are released during normal aggrecan turnover, but increasingly so in disease. We now show that the aggrecan CLD part of the G3 domain activates the classical and to a lesser extent the alternative pathway of complement, via binding of C1q and C3, respectively. The complement control protein (CCP) domain adjacent to the CLD showed no effect on complement initiation. The binding of C1q to G3 depended on ionic interactions and was decreased in D2267N mutant G3. However, the observed complement activation was attenuated due to binding of complement inhibitor factor H to CLD and CCP domains. This was most apparent at the level of deposition of terminal complement components. Taken together our observations indicate aggrecan CLD as one factor involved in the sustained inflammation of the joint.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
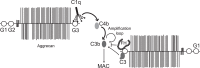
Similar articles
-
Interactions of complement proteins C1q and factor H with lipid A and Escherichia coli: further evidence that factor H regulates the classical complement pathway.Protein Cell. 2011 Apr;2(4):320-32. doi: 10.1007/s13238-011-1029-y. Epub 2011 May 15. Protein Cell. 2011. PMID: 21574022 Free PMC article.
-
A recessive skeletal dysplasia, SEMD aggrecan type, results from a missense mutation affecting the C-type lectin domain of aggrecan.Am J Hum Genet. 2009 Jan;84(1):72-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.12.001. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Am J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19110214 Free PMC article.
-
Native, amyloid fibrils and beta-oligomers of the C-terminal domain of human prion protein display differential activation of complement and bind C1q, factor H and C4b-binding protein directly.Mol Immunol. 2008 Jun;45(11):3213-21. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.02.023. Epub 2008 Apr 11. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18406463
-
Interactions of the humoral pattern recognition molecule PTX3 with the complement system.Immunobiology. 2012 Nov;217(11):1122-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.07.004. Immunobiology. 2012. PMID: 22964239 Review.
-
Canonical and noncanonical functions of complement in systemic lupus erythematosus.Eur J Immunol. 2024 Jul;54(7):e2350918. doi: 10.1002/eji.202350918. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38629181 Review.
Cited by
-
Complement as a Therapeutic Target in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases.Cells. 2021 Jan 13;10(1):148. doi: 10.3390/cells10010148. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33451011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix regulation of inflammation in the healthy and injured spinal cord.Exp Neurol. 2014 Aug;258:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.11.020. Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25017885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoarthritis and the Complement Cascade.Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2018 Jan 3;11:1179544117751430. doi: 10.1177/1179544117751430. eCollection 2018. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2018. PMID: 29434479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Contributions to Osteoarthritis.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017 Dec;15(6):593-600. doi: 10.1007/s11914-017-0411-y. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017. PMID: 29098574 Review.
-
ADAMTS-9 in Mouse Cartilage Has Aggrecanase Activity That Is Distinct from ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 29;20(3):573. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030573. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30699963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sjoberg AP, Trouw LA, Blom AM (2009) Complement activation and inhibition: a delicate balance. Trends Immunol 30: 83–90. - PubMed
-
- Okroj M, Heinegard D, Holmdahl R, Blom AM (2007) Rheumatoid arthritis and the complement system. Ann Med 39: 517–530. - PubMed
-
- Kojouharova M, Reid K, Gadjeva M (2010) New insights into the molecular mechanisms of classical complement activation. Mol Immunol 47: 2154–2160. - PubMed
-
- Groeneveld TW, Oroszlan M, Owens RT, Faber-Krol MC, Bakker AC, et al. (2005) Interactions of the extracellular matrix proteoglycans decorin and biglycan with C1q and collectins. J Immunol 175: 4715–4723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

