Endocytoscopic visualization of squamous cell islands within Barrett's epithelium
- PMID: 23596541
- PMCID: PMC3627841
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i4.174
Endocytoscopic visualization of squamous cell islands within Barrett's epithelium
Abstract
Aim: To study the endocytoscopic visualization of squamous cell islands within Barrett's epithelium.
Methods: Endocytoscopy (ECS) has been studied in the surveillance of Barrett's esophagus, with controversial results. In initial studies, however, a soft catheter type endocytoscope was used, while only methylene blue dye was used for the staining of Barrett's mucosa. Integrated type endocytoscopes (GIF-Q260 EC, Olympus Corp, Tokyo, Japan) have been recently developed, with the incorporation of a high-power magnifying endocytoscope into a standard endoscope together with narrow-band imaging (NBI). Moreover, double staining with a mixture of 0.05% crystal violet and 0.1% of methylene blue (CM) during ECS enables higher quality images comparable to conventional hematoxylin eosin histopathological images.
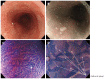
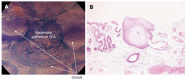
Results: In vivo endocytoscopic visualization of papillary squamous cell islands within glandular Barrett's epithelium in a patient with long-segment Barrett's esophagus is reported. Conventional white light endoscopy showed typical long-segment Barrett's esophagus, with small squamous cell islands within normal Barrett's mucosa, which were better visualized by NBI endoscopy. ECS after double CM staining showed regular Barrett's esophagus, while higher magnification (× 480) revealed the orifices of glandular structures better. Furthermore, typical squamous cell papillary protrusion, classified as endocytoscopic atypia classification (ECA) 2 according to ECA, was identified within regular glandular Barrett's mucosa. Histological examination of biopsies taken from the same area showed squamous epithelium within glandular Barrett's mucosa, corresponding well to endocytoscopic findings.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first report of in vivo visualization of esophageal papillary squamous cell islands surrounded by glandular Barrett's epithelium.
Keywords: Barrett’s esophagus; Crystal violet; Endocytoscopic atypia classification; Endocytoscopy; Hematoxylin eosin stain; Methylene blue; Surveillance.
Figures
References
-
- Inoue H, Yokoyama A, Kudo SE. [Ultrahigh magnifying endoscopy: development of CM double staining for endocytoscopy and its safety] Nihon Rinsho. 2010;68:1247–1252. - PubMed
-
- Minami H, Inoue H, Yokoyama A, Ikeda H, Satodate H, Hamatani S, Haji A, Kudo S. Recent advancement of observing living cells in the esophagus using CM double staining: endocytoscopic atypia classification. Dis Esophagus. 2012;25:235–241. - PubMed
-
- Kumagai Y, Kawada K, Yamazaki S, Iida M, Ochiai T, Momma K, Odajima H, Kawachi H, Nemoto T, Kawano T, et al. Endocytoscopic observation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig Endosc. 2010;22:10–16. - PubMed
-
- Kudo SE, Wakamura K, Ikehara N, Mori Y, Inoue H, Hamatani S. Diagnosis of colorectal lesions with a novel endocytoscopic classification - a pilot study. Endoscopy. 2011;43:869–875. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

