What's new about inflammatory bowel diseases in Ischemic colitis induced by the newly reformulated multicomponent weight-loss supplement Hydroxycut(®)
- PMID: 23596542
- PMCID: PMC3627842
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v5.i4.180
What's new about inflammatory bowel diseases in Ischemic colitis induced by the newly reformulated multicomponent weight-loss supplement Hydroxycut(®)
Abstract
Ischemic colitis accounts for 6%-18% of causes of acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. It is more often multifactorial and more common in elderly. Drugs are considered important causative agents of this disease with different mechanisms. In this paper, we describe a 37-year-old otherwise healthy female presented with sudden onset diffuse abdominal pain and bloody stool. Radiologic, colonoscopic and histopathologic findings were all consistent with ischemic colitis. Her only suspected factor was hydroxycut which she had been taking for a period of 1 mo prior to her presentation. Her condition improved uneventfully after cessation of hydroxycut, bowel rest, intravenous hydration, and antibiotics. This is a first case of ischemic colitis with clear relationship with hydroxycut use (Naranjo score of 7). Our case demonstrates the importance of questioning patients regarding the usage of dietary supplements; especially since many patients consider them safe and do not disclose their use voluntarily to their physicians. Hydroxycut has to be considered as a potential trigger for otherwise unexplained ischemic colitis.
Keywords: Colonoscopy; Gastrointestinal bleeding; Herbal; Hydroxycut; Ischemic colitis; Weight-loss supplement.
Figures
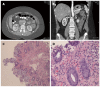
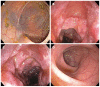
References
-
- Strate LL. Lower GI bleeding: epidemiology and diagnosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2005;34:643–664. - PubMed
-
- Stamatakos M, Douzinas E, Stefanaki C, Petropoulou C, Arampatzi H, Safioleas C, Giannopoulos G, Chatziconstantinou C, Xiromeritis C, Safioleas M. Ischemic colitis: surging waves of update. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2009;218:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Sherid M, Ehrenpreis ED. Types of colitis based on histology. Dis Mon. 2011;57:457–489. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PM, Bloom B, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. Natl Health Stat Report. 2008;(12):1–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

