Time-dependent changes of erectile function in diabetic rats: role of systemic endothelial dysfunction
- PMID: 23596598
- PMCID: PMC3623519
- DOI: 10.5534/wjmh.2012.30.2.114
Time-dependent changes of erectile function in diabetic rats: role of systemic endothelial dysfunction
Abstract
Purpose: To understand the potential contribution of systemic endothelial dysfunction to diabetic erectile dysfunction, and the time course of erectile dysfunction in a streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat model.
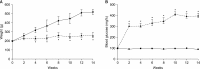
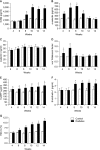
Materials and methods: Among 84, 12-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats, 48 rats received intraperitoneal STZ and were classified into six groups of diabetes by the period of observation (n=8). The remaining 36 rats were also grouped, similar to the diabetic groups, and served as normal controls. After 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 14 weeks of diabetes (serum glucose >250 mg%), all rats underwent cavernous nerve electrostimulation (3 V, 0.2 ms, 30 sec) with varying frequency (2.5~20 Hz). At the end of the study, 8 ml of blood was taken to measure the plasma markers of endothelial function and glycosylated hemoglobin.
Results: Compared to the control, significant reduction of erectile response was not observed until eight weeks after diabetes induction. The diabetic rats had elevation of all plasma markers except for l-selectin. However, the correlation analysis revealed that no systemic marker of endothelial dysfunction was associated with change in erectile function. Only the level of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) showed a modest but significant correlation with the peak intracavernosal pressure, corrected by mean arterial pressure (ρ=-0.183), and the area under the curve of the cavernosometry (ρ=-0.207).
Conclusions: Significant reduction of erectile function was not observed until eight weeks after the induction of diabetes. Except for HbA1c, there was no systemic marker associated with endothelial activation and erectile function in the diabetic rats.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Endothelium; Erectile dysfunction; Rats.
Figures
References
-
- Selvin E, Burnett AL, Platz EA. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in the US. Am J Med. 2007;120:151–157. - PubMed
-
- Saenz de Tejada I, Goldstein I, Azadzoi K, Krane RJ, Cohen RA. Impaired neurogenic and endothelium-mediated relaxation of penile smooth muscle from diabetic men with impotence. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:1025–1030. - PubMed
-
- De Angelis L, Marfella MA, Siniscalchi M, Marino L, Nappo F, Giugliano F, et al. Erectile and endothelial dysfunction in Type II diabetes: a possible link. Diabetologia. 2001;44:1155–1160. - PubMed
-
- Pegge NC, Twomey AM, Vaughton K, Gravenor MB, Ramsey MW, Price DE. The role of endothelial dysfunction in the pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction in diabetes and in determining response to treatment. Diabet Med. 2006;23:873–878. - PubMed
-
- Ahn GJ, Yu JY, Choi SM, Kang KK, Ahn BO, Kwon JW, et al. Chronic administration of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor improves erectile and endothelial function in a rat model of diabetes. Int J Androl. 2005;28:260–266. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
