Heart failure in East Asia
- PMID: 23597295
- PMCID: PMC3682395
- DOI: 10.2174/1573403x11309020004
Heart failure in East Asia
Abstract
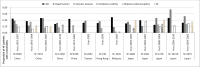
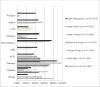
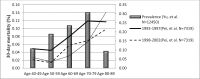
Heart failure (HF) carries a major burden of disease in East Asia, with high associated risk of mortality and morbidity. In recent decades, the epidemiology of HF has changed with social and economical development in East Asia. The burden of HF is still severe in East Asia. The prevalence of HF ranges from 1.3% to 6.7% throughout the region. As aetiological factors, ischaemic heart disease has increased and valvular disease reduced in most East Asian countries. Diuretics are the most commonly used drugs (51.0%-97%), followed by renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors (59%-77%), with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, ACEI, (32%-52%) and has angiotensin-2 receptor blockers, ARBs (31%-44%) in similar proportions. Betablocker use has also increased in recent years. Total mortality from HF ranges from 2% to 9% in China, Taiwan, Singapore, Thailand, and Japan. Age>65 years, diabetes mellitus, anaemia, renal dysfunction and atrial fibrillation (AF) are associated with adverse outcome. More prospective, region-specific data are still required, particularly regarding new drug therapies such as eplerenone and ivabradine.
Figures
References
-
- Gheorghiade M, Pang PS. Acute heart failure syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:557–73. - PubMed
-
- National Clinical Guideline Centre (UK).Chronic Heart Failure: National Clinical Guideline for Diagnosis and Management in Primary and Secondary Care. Partial Update [Internet].London: Royal College of Physicians (UK) Aug. http//www.ncbi. nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK65340/ 2010. - PubMed
-
- Norton C, Georgiopoulou VV, Kalogeropoulos AP. Epidemiology and cost of advanced heart failure. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;54:78–85. - PubMed
-
- Report on cardiovascular diseases in China.Hu Shengshou. Kong Lingzhi editors. National Center of Cardiovascular Diseases Encyclopdia of China Publishing House. 2012
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
