Structural insights into LINC complexes
- PMID: 23597672
- PMCID: PMC4077334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.03.005
Structural insights into LINC complexes
Abstract
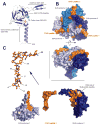
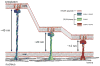
Communication between nucleus and cytoplasm extends past molecular exchange and critically includes mechanical wiring. Cytoskeleton and nucleoskeleton are connected via molecular tethers that span the nuclear envelope. Sad1, UNC84 (SUN)-domain proteins spanning the inner nuclear membrane and Klarsicht, ANC-1 and SYNE/Nesprin-1 and -2 Homology (KASH)-peptide bearing proteins residing in the outer nuclear membrane directly bind and constitute the core of the LInkers of Nucleoskeleton and Cytoskeleton (LINC) complex. These connections appear critical for a growing number of biological processes and aberrations are implicated in a host of diverse diseases, including muscular dystrophies, cardiomyopathies, and premature aging. We discuss recent developments in this vibrant research area, particularly in context of first structural insights into LINC complexes reported in the past year.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

