Fungal cell wall dynamics and infection site microenvironments: signal integration and infection outcome
- PMID: 23597789
- PMCID: PMC3755087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.03.003
Fungal cell wall dynamics and infection site microenvironments: signal integration and infection outcome
Abstract
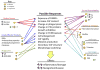
Upon entrance into the host, fungi encounter a myriad of host effector products and microenvironments that they sense and adapt to for survival. Alterations of the structure and composition of the cell wall is a major fungal adaptation mechanism to evade these environments. Here we discuss recent findings of host-microenvironmental induced fungal cell wall changes, including structure, composition, and protein content, and their effects on host immune responses. A take home message from these recent studies is an emerging understanding of how integration of multiple signals, of both fungal and host responses to dynamic infection site microenvironments, determines outcomes of infection. A challenge moving forward is to further understand these mechanisms and harness them for therapeutic benefit.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Latge JP. Tasting the fungal cell wall. Cell Microbiol. 2010;12:863–872. - PubMed
-
- Gupta AO, Singh N. Immune reconstitution syndrome and fungal infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2011;24:527–533. - PubMed
-
- Fontaine T, Delangle A, Simenel C, Coddeville B, van Vliet SJ, van Kooyk Y, Bozza S, Moretti S, Schwarz F, Trichot C, et al. Galactosaminogalactan, a new immunosuppressive polysaccharide of Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002372. Important paper describing the discovery of a potent immunosuppressive polysaccharide found in the cell wall of Aspergillus fumigatus. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

