Alternative sources of omega-3 fats: can we find a sustainable substitute for fish?
- PMID: 23598439
- PMCID: PMC3705349
- DOI: 10.3390/nu5041301
Alternative sources of omega-3 fats: can we find a sustainable substitute for fish?
Abstract
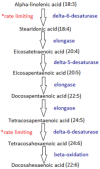
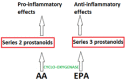
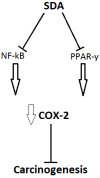
Increasing demand for eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) containing fish oils is putting pressure on fish species and numbers. Fisheries provide fish for human consumption, supplement production and fish feeds and are currently supplying fish at a maximum historical rate, suggesting mass-scale fishing is no longer sustainable. However, the health properties of EPA and DHA long-chain (LC) omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) demonstrate the necessity for these oils in our diets. EPA and DHA from fish oils show favourable effects in inflammatory bowel disease, some cancers and cardiovascular complications. The high prevalence of these diseases worldwide indicates the requirement for alternative sources of LC-PUFA. Strategies have included plant-based fish diets, although this may compromise the health benefits associated with fish oils. Alternatively, stearidonic acid, the product of α-linolenic acid desaturation, may act as an EPA-enhancing fatty acid. Additionally, algae oils may be a promising omega-3 PUFA source for the future. Algae are beneficial for multiple industries, offering a source of biodiesel and livestock feeds. However, further research is required to develop efficient and sustainable LC-PUFA production from algae. This paper summarises the recent research for developing prospective substitutes for omega-3 PUFA and the current limitations that are faced.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is the world supply of omega-3 fatty acids adequate for optimal human nutrition?Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015 Mar;18(2):147-54. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000145. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015. PMID: 25635599 Review.
-
DHA-containing oilseed: a timely solution for the sustainability issues surrounding fish oil sources of the health-benefitting long-chain omega-3 oils.Nutrients. 2014 May 22;6(5):2035-58. doi: 10.3390/nu6052035. Nutrients. 2014. PMID: 24858407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stearidonic acid as a supplemental source of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids to enhance status for improved human health.Nutrition. 2013 Feb;29(2):363-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.06.003. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Nutrition. 2013. PMID: 23102888 Review.
-
Microbial and genetically engineered oils as replacements for fish oil in aquaculture feeds.Biotechnol Lett. 2017 Nov;39(11):1599-1609. doi: 10.1007/s10529-017-2402-6. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Biotechnol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28721583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replacement of Marine Fish Oil with de novo Omega-3 Oils from Transgenic Camelina sativa in Feeds for Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata L.).Lipids. 2016 Oct;51(10):1171-1191. doi: 10.1007/s11745-016-4191-4. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Lipids. 2016. PMID: 27590240 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Validation of endogenous reference genes in Buglossoides arvensis for normalizing RT-qPCR-based gene expression data.Springerplus. 2015 Apr 15;4:178. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-0952-4. eCollection 2015. Springerplus. 2015. PMID: 25918683 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of microalgal polyunsaturated fatty acid oil on body weight and lipid accumulation in the liver of C57BL/6 mice fed a high fat diet.J Biomed Res. 2016 May;30(3):234-42. doi: 10.7555/JBR.30.2016K0004. Epub 2016 Apr 10. J Biomed Res. 2016. PMID: 27533934 Free PMC article.
-
Biotechnological production of omega-3 fatty acids: current status and future perspectives.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 7;14:1280296. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1280296. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlations between growth and wool quality traits of genetically divergent Australian lambs in response to canola or flaxseed oil supplementation.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 3;14(1):e0208229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208229. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30605467 Free PMC article.
-
The glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase PLAT2 functions in the generation of DHA-rich glycerolipids in Aurantiochytrium limacinum F26-b.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 30;14(1):e0211164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211164. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30699157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calder P. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006;83:1505–1519. - PubMed
-
- Guil-Guerrero J.L. Stearidonic acid (18:4n-3): Metabolism, nutritional importance, medical uses and natural sources. Eur. J. Lipid. Sci. Technol. 2007;109:1226–1236. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.200700207. - DOI
-
- Simopoulos A. Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2002;21:495–505. - PubMed
-
- Dulvy N.K., Sadovy Y., Reynolds J.D. Extinction vulnerability in marine populations. Fish Fish. 2003;4:25–64. doi: 10.1046/j.1467-2979.2003.00105.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

