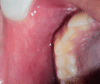
940 nm diode laser therapy in management of recurrent apthous ulcer
- PMID: 23598930
- PMCID: PMC3644907
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-008489
940 nm diode laser therapy in management of recurrent apthous ulcer
Abstract
Recurrent apthous stomatitis (RAS) is one of the most common oral inflammatory diseases characterised by painful recurrent ulcerations of the orofacial region. The ulcers occur in three clinical forms: minor, major and herpetiform. Several therapies have been advocated to manage these lesions such as topical corticosteroids (triamcinolone acetonide, hydrocortisone acetate and clobetasol propionate), chlorhexidine mouth rinses, tetracycline oral rinses, thalidomide, fluocinonide, colchicines and the immune boosting agent levamosile, vitamin therapy and topical interferon α-2a. Laser therapy is used as an alternative method in treatment of RAS. In this paper one patient with RAS was treated using a 940 nm diode laser for symptomatic relief of pain and burning sensation and healing of ulcer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of laser irradiation on aphthae pain management: A four different wavelengths comparison.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018 Dec;189:1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.09.016. Epub 2018 Sep 20. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018. PMID: 30268950
-
Treatment of recurrent minor aphthous stomatitis using diode laser (940 nm).J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 21;28(2):e99-e112. doi: 10.47750/jptcp.2022.864. eCollection 2022. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35213109 Clinical Trial.
-
Photobiomodulation in recurrent aphthous stomatitis management using three different laser wavelengths. A randomized clinical trial.Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Nov 19;39(1):285. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-04236-3. Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39557704 Clinical Trial.
-
Management strategies for HIV-associated aphthous stomatitis.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(10):669-80. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200304100-00002. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 14507229 Review.
-
[Aphthous ulcers and oral ulcerations].Presse Med. 2016 Feb;45(2):215-26. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2016.01.005. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Presse Med. 2016. PMID: 26880080 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Low-level laser therapy in the treatment of recurrent aphthous ulcers: a systematic review.ScientificWorldJournal. 2015;2015:150412. doi: 10.1155/2015/150412. Epub 2015 Mar 23. ScientificWorldJournal. 2015. PMID: 25879049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colvard M, Kuo P. Managing apthous ulcers: laser treatment applied. J Am Dent Assoc 1991;2013:51–3 - PubMed
-
- De Souza TOF, et al. Clinical evaluation of low-level laser treatment for recurring apthous stomatitis. Photomed Laser Surg 2010;2013(s2):1–8 - PubMed
-
- Tezel A, Kara C, Balkaya V, et al. An evaluation of different treatments for recurrent apthous stomatitis and patient perceptions: Nd:YAG laser versus medication. Photomed Laser Surg 2009;2013:101–6 - PubMed
-
- Sharon-Buller A, Sela M. CO2 -laser treatment of ulcerative lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2004;2013:332–4 - PubMed
-
- Zand N, et al. Relieving pain in minor apthous stomatitis by a single session of non-thermal carbon dioxide laser irradiation. Lasers Med Sci 2009;2013:515–20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical