Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase-Associated Ribonuclease H Activity
- PMID: 23599900
- PMCID: PMC3627382
- DOI: 10.3390/biology1030521
Inhibitors of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase-Associated Ribonuclease H Activity
Abstract
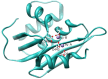
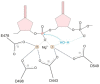
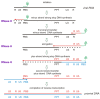
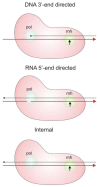
HIV-1 enzyme reverse transcriptase (RT) is a major target for antiviral drug development, with over half of current FDA-approved therapeutics against HIV infection targeting the DNA polymerase activity of this enzyme. HIV-1 RT is a multifunctional enzyme that has RNA and DNA dependent polymerase activity, along with ribonuclease H (RNase H) activity. The latter is responsible for degradation of the viral genomic RNA template during first strand DNA synthesis to allow completion of reverse transcription and the viral dsDNA. While the RNase H activity of RT has been shown to be essential for virus infectivity, all currently used drugs directed at RT inhibit the polymerase activity of the enzyme; none target RNase H. In the last decade, the increasing prevalence of HIV variants resistant to clinically used antiretrovirals has stimulated the search for inhibitors directed at stages of HIV replication different than those targeted by current drugs. HIV RNase H is one such novel target and, over the past few years, significant progress has been made in identifying and characterizing new RNase H inhibitor pharmacophores. In this review we focus mainly on the most potent low micromolar potency compounds, as these provide logical bases for further development. We also discuss why HIV RNase H has been a difficult target for antiretroviral drug development.
Keywords: HIV-1; reverse transcription; ribonuclease H (RNase H); ribonuclease H inhibitor (RNHI).
Figures

References
-
- Huang H., Chopra R., Verdine G.L., Harrison S.C. Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug resistance. Science. 1998;282:1669–1675. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
