Epithelial expression of interleukin-37b in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 23600829
- PMCID: PMC3646440
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12061
Epithelial expression of interleukin-37b in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
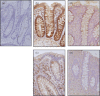
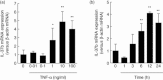
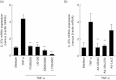
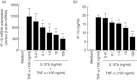
Interleukin (IL)-37 is a member of the IL-1 cytokine family. We investigated IL-37b expression in the inflamed mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. Furthermore, we analysed IL-37b expression in human colonic epithelial cells. The human colonic epithelial cell line T84 and human colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts (SEMFs) were used. IL-37b expression in the IBD mucosa was evaluated by immunohistochemistry. IL-37b mRNA and protein expression were determined by real time-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Western blotting, respectively. IL-37b was not detected in the normal colonic mucosa. In the inflamed mucosa of IBD patients, epithelial IL-37b expression was increased markedly. In ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) patients, IL-37b expression was enhanced in the affected mucosa. In the intestinal epithelial cell line T84, the expression of IL-37b mRNA and protein was enhanced by tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α. This IL-37b induction by TNF-α was mediated by nuclear factor (NF)-κB and activator protein (AP)-1 activation. Furthermore, IL-37b inhibited TNF-α-induced interferon-γ-inducible protein (IP)-10 expression significantly in human colonic SEMFs. Epithelial IL-37b expression was increased in IBD patients, especially UC patients. IL-37b may be involved in the pathophysiology of IBD as an anti-inflammatory cytokine and an inhibitor of both innate and acquired immune responses.
© 2013 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

References
-
- Mayer L. Evolving paradigms in the pathogenesis of IBD. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Andoh A, Imaeda H, Aomatsu T, et al. Comparison of the fecal microbiota profiles between ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease using terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:479–486. - PubMed
-
- Andoh A, Kuzuoka H, Tsujikawa T, et al. Multicenter analysis of fecal microbiota profiles in Japanese patients with Crohn's disease. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:1298–1307. - PubMed
-
- Kobori A, Yagi Y, Imaeda H, et al. Interleukin-33 expression is specifically enhanced in inflamed mucosa of ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:999–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

