Pseudomonas aeruginosa disrupts Caenorhabditis elegans iron homeostasis, causing a hypoxic response and death
- PMID: 23601103
- PMCID: PMC3641844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.03.003
Pseudomonas aeruginosa disrupts Caenorhabditis elegans iron homeostasis, causing a hypoxic response and death
Abstract
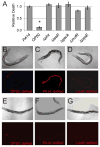
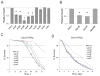
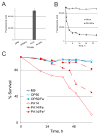
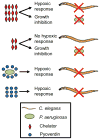
The opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes serious human infections, but effective treatments and the mechanisms mediating pathogenesis remain elusive. Caenorhabditis elegans shares innate immune pathways with humans, making it invaluable to investigate infection. To determine how P. aeruginosa disrupts host biology, we studied how P. aeruginosa kills C. elegans in a liquid-based pathogenesis model. We found that P. aeruginosa-mediated killing does not require quorum-sensing pathways or host colonization. A chemical genetic screen revealed that iron chelators alleviate P. aeruginosa-mediated killing. Consistent with a role for iron in P. aeruginosa pathogenesis, the bacterial siderophore pyoverdin was required for virulence and was sufficient to induce a hypoxic response and death in the absence of bacteria. Loss of the C. elegans hypoxia-inducing factor HIF-1, which regulates iron homeostasis, exacerbated P. aeruginosa pathogenesis, further linking hypoxia and killing. As pyoverdin is indispensable for virulence in mice, pyoverdin-mediated hypoxia is likely to be relevant in human pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
C. elegans SWAN-1 Binds to EGL-9 and regulates HIF-1-mediated resistance to the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Aug 26;6(8):e1001075. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001075. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20865124 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Immune Modulators Enhance Caenorhabditis elegans Resistance to Multiple Pathogens.mSphere. 2021 Jan 6;6(1):e00950-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00950-20. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 33408224 Free PMC article.
-
Selenite enhances immune response against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 via SKN-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 22;9(8):e105810. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105810. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25147937 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans: a model genetic host to study Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000 Feb;3(1):29-34. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(99)00047-8. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10679415 Review.
-
Modeling Host-Pathogen Interactions in C. elegans: Lessons Learned from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 27;25(13):7034. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137034. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction, aging, and the mitochondrial unfolded protein response in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2022 Nov 30;222(4):iyac160. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac160. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 36342845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyoverdine Inhibitors and Gallium Nitrate Synergistically Affect Pseudomonas aeruginosa.mSphere. 2021 Jun 30;6(3):101128msphere0040121. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00401-21. Epub 2021 Jun 16. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34133200 Free PMC article.
-
l-Ornithine-N5-monooxygenase (PvdA) Substrate Analogue Inhibitors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections Treatment: Drug Repurposing Computational Studies.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 25;12(7):887. doi: 10.3390/biom12070887. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883443 Free PMC article.
-
Examining Sporadic Cancer Mutations Uncovers a Set of Genes Involved in Mitochondrial Maintenance.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;14(5):1009. doi: 10.3390/genes14051009. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239369 Free PMC article.
-
Insect-derived cecropins display activity against Acinetobacter baumannii in a whole-animal high-throughput Caenorhabditis elegans model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Mar;59(3):1728-37. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04198-14. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25583713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldwin DA, Jenny ER, Aisen P. The effect of human serum transferrin and milk lactoferrin on hydroxyl radical formation from superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1984;259:13391–13394. - PubMed
-
- Bumann D. Has nature already identified all useful antibacterial targets? Current opinion in microbiology. 2008;11:387–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

