Chronic sinusitis pathophysiology: the role of allergy
- PMID: 23601202
- PMCID: PMC3781389
- DOI: 10.2500/ajra.2013.27.3906
Chronic sinusitis pathophysiology: the role of allergy
Abstract
Background: Chronic hyperplastic eosinophilic sinusitis (CHES) is an inflammatory disease characterized by eosinophil infiltration of sinus tissue that can present with and without nasal polyps (NPs). Aeroallergen sensitization in CHES occurs regularly, but the causality between allergen sensitivity, exposure, and disease is unclear.
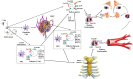
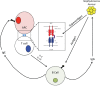
Methods: Allergen is unlikely to directly enter healthy sinuses either by diffusion or ciliary flow, and, even this is more problematic given the loss of patency of the ostia of diseased sinuses. Inflammation and tissue eosinophilia can develop secondary to allergen exposure in the nares, with systemic humoral recirculation of allergic cells including eosinophils, Th2 lymphocytes, and eosinophil precursors that are nonspecifically recruited back to the diseased sinuses.
Results: The possibility of an allergic reaction to peptides derived from bacteria (i.e., Staphylococcus or superantigens) or fungi that colonize the diseased sinus also provides a plausible allergic mechanism.
Conclusion: Treatments of this disease include agents directed at allergic mediators such as leukotriene modifiers and corticosteroids, although this does not necessarily signify that an IgE-dependent mechanism can be ascribed. However, more recently, omalizumab has shown promise, including in patients without obvious aeroallergen sensitization. Although many aspects of the role of allergy in CHES remain a mystery, the mechanisms that are being elucidated allow for improved understanding of this disease, which ultimately will lead to better treatments for our patients who live daily with this disease.
Figures
References
-
- Payne SC, Borish L, Steinke JW. Genetics and phenotyping in chronic sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:710–720, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Hamilos DL, Leung DY, Wood R, et al. Eosinophil infiltration in nonallergic chronic hyperplastic sinusitis with nasal polyposis (CHS/NP) is associated with endothelial VCAM-1 upregulation and expression of TNF-alpha. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 15:443–450, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Rachelefsky GS. National guidelines needed to manage rhinitis and prevent complications. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 82:296–305, 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

