Platelet motion near a vessel wall or thrombus surface in two-dimensional whole blood simulations
- PMID: 23601323
- PMCID: PMC3628562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.01.061
Platelet motion near a vessel wall or thrombus surface in two-dimensional whole blood simulations
Abstract
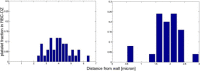
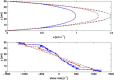
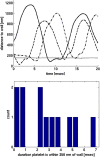
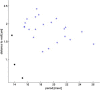
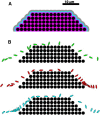
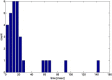
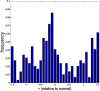
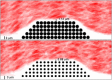
Computational simulations using a two-dimensional lattice-Boltzmann immersed boundary method were conducted to investigate the motion of platelets near a vessel wall and close to an intravascular thrombus. Physiological volume fractions of deformable red blood cells and rigid platelet-size elliptic particles were studied under arteriolar flow conditions. Tumbling of platelets in the red-blood-cell depleted zone near the vessel walls was strongly influenced by nearby red blood cells. The thickness of the red-blood-cell depleted zone was greatly reduced near a thrombus, and platelets in this zone were pushed close to the surface of the thrombus to distances that would facilitate their cohesion to it. The distance, nature, and duration of close platelet-thrombus encounters were influenced by the porosity of the thrombus. The strong influence on platelet-thrombus encounters of red-blood-cell motion and thrombus porosity must be taken into account to understand the dynamics of platelet attachment to a growing thrombus.
Copyright © 2013 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
On the simultaneous motions of many blood cells.Biophys J. 2013 May 7;104(9):1839. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.03.045. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23663823 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Rheological factors in platelet - vessel wall interactions.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Aug 18;294(1072):251-66. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0104. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981. PMID: 6117889
-
A three-dimensional multiscale model for the prediction of thrombus growth under flow with single-platelet resolution.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Jan 28;18(1):e1009850. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009850. eCollection 2022 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35089923 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet dynamics in three-dimensional simulation of whole blood.Biophys J. 2014 Jun 3;106(11):2529-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.04.028. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24896133 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-vessel wall interaction in health and disease.Neth J Med. 2010 Jun;68(6):242-51. Neth J Med. 2010. PMID: 20558854 Review.
-
Platelet response heterogeneity in thrombus formation.Thromb Haemost. 2009 Dec;102(6):1149-56. doi: 10.1160/TH09-05-0289. Thromb Haemost. 2009. PMID: 19967145 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive study on different modelling approaches to predict platelet deposition rates in a perfusion chamber.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 22;5:13606. doi: 10.1038/srep13606. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26391513 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology of platelet-vessel wall interactions.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;844:85-98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2095-2_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25480638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Risks of Philadelphia-Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms at Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital.J Blood Med. 2022 Sep 12;13:495-503. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S374636. eCollection 2022. J Blood Med. 2022. PMID: 36118738 Free PMC article.
-
Numerical Simulation in Microvessels for the Design of Drug Carriers with the Immersed Boundary-Lattice Boltzmann Method.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 Mar 28;16(4):389. doi: 10.3390/mi16040389. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283266 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-cellular modeling of platelet transport in blood flow through microchannels with constriction.Soft Matter. 2016 May 11;12(19):4339-51. doi: 10.1039/c6sm00154h. Soft Matter. 2016. PMID: 27087267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fogelson A.L., Guy R.D. Platelet-wall interactions in continuum models of platelet thrombosis: formulation and numerical solution. Math. Med. Biol. 2004;21:293–334. - PubMed
-
- Fogelson A.L., Tania N. Coagulation under flow: the influence of flow-mediated transport on the initiation and inhibition of coagulation. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005;34:91–108. - PubMed
-
- Jackson S.P. The growing complexity of platelet aggregation. Blood. 2007;109:5087–5095. - PubMed
-
- Tilles A.W., Eckstein E.C. The near-wall excess of platelet-sized particles in blood flow: its dependence on hematocrit and wall shear rate. Microvasc. Res. 1987;33:211–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

