Platelet motion near a vessel wall or thrombus surface in two-dimensional whole blood simulations
- PMID: 23601323
- PMCID: PMC3628562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.01.061
Platelet motion near a vessel wall or thrombus surface in two-dimensional whole blood simulations
Abstract
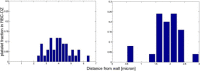
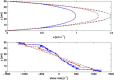
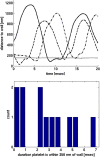
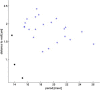
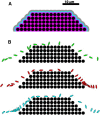
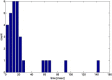
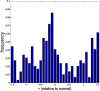
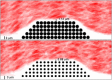
Computational simulations using a two-dimensional lattice-Boltzmann immersed boundary method were conducted to investigate the motion of platelets near a vessel wall and close to an intravascular thrombus. Physiological volume fractions of deformable red blood cells and rigid platelet-size elliptic particles were studied under arteriolar flow conditions. Tumbling of platelets in the red-blood-cell depleted zone near the vessel walls was strongly influenced by nearby red blood cells. The thickness of the red-blood-cell depleted zone was greatly reduced near a thrombus, and platelets in this zone were pushed close to the surface of the thrombus to distances that would facilitate their cohesion to it. The distance, nature, and duration of close platelet-thrombus encounters were influenced by the porosity of the thrombus. The strong influence on platelet-thrombus encounters of red-blood-cell motion and thrombus porosity must be taken into account to understand the dynamics of platelet attachment to a growing thrombus.
Copyright © 2013 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
On the simultaneous motions of many blood cells.Biophys J. 2013 May 7;104(9):1839. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.03.045. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23663823 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fogelson A.L., Guy R.D. Platelet-wall interactions in continuum models of platelet thrombosis: formulation and numerical solution. Math. Med. Biol. 2004;21:293–334. - PubMed
-
- Fogelson A.L., Tania N. Coagulation under flow: the influence of flow-mediated transport on the initiation and inhibition of coagulation. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005;34:91–108. - PubMed
-
- Jackson S.P. The growing complexity of platelet aggregation. Blood. 2007;109:5087–5095. - PubMed
-
- Tilles A.W., Eckstein E.C. The near-wall excess of platelet-sized particles in blood flow: its dependence on hematocrit and wall shear rate. Microvasc. Res. 1987;33:211–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

