Assessment of 0.5 T static field exposure effect on yeast and HEK cells using electrorotation
- PMID: 23601327
- PMCID: PMC3628304
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.01.063
Assessment of 0.5 T static field exposure effect on yeast and HEK cells using electrorotation
Abstract
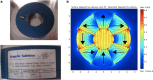
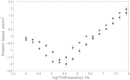
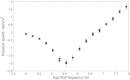
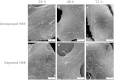
This study aims to examine the influence of a 0.5 T static magnetic field (SMF) on yeast and human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cell using electrorotation (ROT). Following 48 h exposition to the SMF, no difference was noted between ROT spectra of unexposed and exposed yeast cells, which extend previous reports on the absence of SMF effects on yeast. We also compared the ROT spectrum and the extracted electrical characteristics of HEK cells exposed during 72 h to a 0.5 T uniform static magnetic field with those of unexposed cells. SMF potential effects on HEK proliferation kinetics and cell morphology were also assessed by using the trypan blue exclusion method and scanning electron microscopy, respectively. At last, no significant differences were observed between control and exposed HEK cells concerning electrical properties, growth, and morphology.
Copyright © 2013 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Schenck J.F. Safety of strong, static magnetic fields. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2000;12:2–19. - PubMed
-
- Schenck J.F. Physical interactions of static magnetic fields with living tissues. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2005;87:185–204. - PubMed
-
- Miyakoshi J. Effects of static magnetic fields at the cellular level. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2005;87:213–223. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) World Health Organization; Geneva: 2006. Static Fields: Environmental Health Criteria.
-
- Inglis D., Riehn R., Austin R. Microfluidic high gradient magnetic cell separation. J. Appl. Phys. 2006;99 08K101–08K101.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

