Reconstitution of nucleosome demethylation and catalytic properties of a Jumonji histone demethylase
- PMID: 23601638
- PMCID: PMC3704229
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.03.008
Reconstitution of nucleosome demethylation and catalytic properties of a Jumonji histone demethylase
Abstract
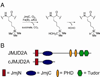
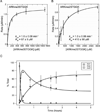
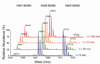
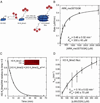
Jumonji histone demethylases catalyze removal of methyl marks from lysine residues in histone proteins within nucleosomes. Here, we show that the catalytic domain of demethylase JMJD2A (cJMJD2A) utilizes a distributive mechanism to remove the histone H3 lysine 9 trimethyl mark. By developing a method to assess demethylation of homogeneous, site-specifically methylated nucleosomes, we determined that the kinetic parameters for demethylation of nucleosomes by cJMJD2A are comparable to those of peptide substrates. These findings imply that other domains of the demethylase or its protein partners may contribute to nucleosome recognition in vivo and, in this way, may further regulate demethylation activity and processivity. The quantitative assays of nucleosome demethylation developed in our work provide a platform for future work with complex chromatin substrates and full-length demethylases.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Berry WL, Shin S, Lightfoot SA, Janknecht R. Oncogenic features of the JMJD2A histone demethylase in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012;41:1701–1706. - PubMed
-
- Cloos PAC, Christensen J, Agger K, Maiolica A, Rappsilber J, Antal T, Hansen KH, Helin K. The putative oncogene GASC1 demethylates tri- and dimethylated lysine 9 on histone H3. Nature. 2006;442:307–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

