Increased survival of cirrhotic patients with septic shock
- PMID: 23601847
- PMCID: PMC4057386
- DOI: 10.1186/cc12687
Increased survival of cirrhotic patients with septic shock
Abstract
Introduction: The overall outcome of septic shock has been recently improved. We sought to determine whether this survival gain extends to the high-risk subgroup of patients with cirrhosis.
Methods: Cirrhotic patients with septic shock admitted to a medical intensive care unit (ICU) during two consecutive periods (1997-2004 and 2005-2010) were retrospectively studied.
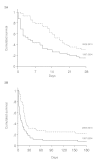
Results: Forty-seven and 42 cirrhotic patients presented with septic shock in 1997-2004 and 2005-2010, respectively. The recent period differed from the previous one by implementation of adjuvant treatments of septic shock including albumin infusion as fluid volume therapy, low-dose glucocorticoids, and intensive insulin therapy. ICU and hospital survival markedly improved over time (40% in 2005-2010 vs. 17% in 1997-2004, P = 0.02 and 29% in 2005-2010 vs. 6% in 1997-2004, P = 0.009, respectively). Furthermore, this survival gain in the latter period was sustained for 6 months (survival rate 24% in 2005-2010 vs. 6% in 1997-2004, P = 0.06). After adjustment with age, the liver disease stage (Child-Pugh score), and the critical illness severity score (SOFA score), ICU admission between 2005 and 2010 remained an independent favorable prognostic factor (odds ratio (OR) 0.09, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.02-0.4, P = 0.004). The stage of the underlying liver disease was also independently associated with hospital mortality (Child-Pugh score: OR 1.42 per point, 95% CI 1.06-1.9, P = 0.018).
Conclusions: In the light of advances in management of both cirrhosis and septic shock, survival of such patients substantially increased over recent years. The stage of the underlying liver disease and the related therapeutic options should be included in the decision-making process for ICU admission.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cirrhotic Patients Admitted to the ICU With Septic Shock: Factors Predicting Short and Long-Term Outcome.Shock. 2019 Oct;52(4):408-413. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001282. Shock. 2019. PMID: 30395082 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of sepsis bundle application and outcomes predictors to cirrhotic patients with septic shock.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 May 26;21(1):483. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06194-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34039297 Free PMC article.
-
Improved prognosis of septic shock in patients with cirrhosis: a multicenter study*.Crit Care Med. 2014 Jul;42(7):1666-75. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000321. Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24732239
-
Temporal changes in management and outcome of septic shock in patients with malignancies in the intensive care unit.Crit Care Med. 2008 Mar;36(3):690-6. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0B013E318165314B. Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18431262
-
The impact of obesity in cirrhotic patients with septic shock: A retrospective cohort study.Liver Int. 2018 Jul;38(7):1230-1241. doi: 10.1111/liv.13648. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Liver Int. 2018. PMID: 29194916
Cited by
-
The Survival of Septic Patients with Compensated Liver Cirrhosis Is Not Inferior to That of Septic Patients without Liver Cirrhosis: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis.J Clin Med. 2022 Mar 15;11(6):1629. doi: 10.3390/jcm11061629. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35329955 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging concepts in the care of patients with cirrhosis and septic shock.World J Hepatol. 2023 Apr 27;15(4):497-514. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i4.497. World J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37206653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timing and causes of death in septic shock.Ann Intensive Care. 2015 Dec;5(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13613-015-0058-8. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Ann Intensive Care. 2015. PMID: 26092499 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the prognosis of cirrhotic patients in the intensive care unit: What we know and what we need to know better.World J Hepatol. 2021 Oct 27;13(10):1341-1350. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i10.1341. World J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34786170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term outcome of patients with liver cirrhosis admitted to a general intensive care unit.Ann Intensive Care. 2017 Dec;7(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0257-6. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Ann Intensive Care. 2017. PMID: 28374334 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moreau R, Hadengue A, Soupison T, Kirstetter P, Mamzer MF, Vanjak D, Vauquelin P, Assous M, Sicot C. Septic shock in patients with cirrhosis: hemodynamic and metabolic characteristics and intensive care unit outcome. Crit Care Med. 1992;17:746–750. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199206000-00008. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical