CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation
- PMID: 23601906
- PMCID: PMC3674206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.03.005
CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation
Abstract
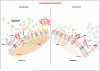
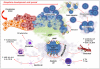
The enzymatic activities of CD39 and CD73 play strategic roles in calibrating the duration, magnitude, and chemical nature of purinergic signals delivered to immune cells through the conversion of ADP/ATP to AMP and AMP to adenosine, respectively. This drives a shift from an ATP-driven proinflammatory environment to an anti-inflammatory milieu induced by adenosine. The CD39/CD73 pathway changes dynamically with the pathophysiological context in which it is embedded. It is becoming increasingly appreciated that altering this catabolic machinery can change the course or dictate the outcome of several pathophysiological events, such as AIDS, autoimmune diseases, infections, atherosclerosis, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and cancer, suggesting these ectoenzymes are novel therapeutic targets for managing a variety of disorders.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Crimeen-Irwin B, et al. Failure of immune homeostasis the consequences of under and over reactivity. Curr. Drug. Targets. Immune. Endocr. Metabol. Disord. 2005;5:413–422. - PubMed
-
- Sitkovsky MV, Ohta A. The `danger' sensors that STOP the immune response: the A2 adenosine receptors? Trends Immunol. 2005;26:299–304. - PubMed
-
- Trautmann A. Extracellular ATP in the immune system: more than just a “danger signal”. Sci. Signal. 2009;2:pe6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

