Mechanisms of sporadic cerebral small vessel disease: insights from neuroimaging
- PMID: 23602162
- PMCID: PMC3836247
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70060-7
Mechanisms of sporadic cerebral small vessel disease: insights from neuroimaging
Erratum in
- Lancet Neurol. 2013 Jun;12(6):532
Abstract
The term cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) describes a range of neuroimaging, pathological, and associated clinical features. Clinical features range from none, to discrete focal neurological symptoms (eg, stroke), to insidious global neurological dysfunction and dementia. The burden on public health is substantial. The pathogenesis of SVD is largely unknown. Although the pathological processes leading to the arteriolar disease are associated with vascular risk factors and are believed to result from an intrinsic cerebral arteriolar occlusive disease, little is known about how these processes result in brain disease, how SVD lesions contribute to neurological or cognitive symptoms, and the association with risk factors. Pathology often shows end-stage disease, which makes identification of the earliest stages difficult. Neuroimaging provides considerable insights; although the small vessels are not easily seen themselves, the effects of their malfunction on the brain can be tracked with detailed brain imaging. We discuss potential mechanisms, detectable with neuroimaging, that might better fit the available evidence and provide testable hypotheses for future study.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
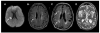


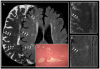
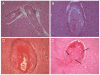
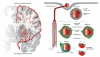
Comment in
-
Microbleeds in cerebral small vessel disease.Lancet Neurol. 2013 Aug;12(8):735-6. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70148-0. Lancet Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23867194 No abstract available.
-
Microbleeds in cerebral small vessel disease - authors' reply.Lancet Neurol. 2013 Aug;12(8):736-7. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70152-2. Lancet Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23867195 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:689–701. - PubMed
-
- Bullmore E, Sporns O. The economy of brain network organization. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:336–49. - PubMed
-
- van der Flier WM, van Straaten EC, Barkhof F, et al. Small vessel disease and general cognitive function in nondisabled elderly: the LADIS study. Stroke. 2005;36:2116–20. - PubMed
-
- Herrmann LL, Le Masurier M, Ebmeier KP. White matter hyperintensities in late life depression: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79:619–24. - PubMed
-
- de Laat KF, Tuladhar AM, van Norden AGW, Norris DG, Zwiers MP, de Leeuw F-E. Loss of white matter integrity is associated with gait disorders in cerebral small vessel disease. Brain. 2011;134:73–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

