Skin blood flow dynamics and its role in pressure ulcers
- PMID: 23602509
- PMCID: PMC3658615
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtv.2013.03.001
Skin blood flow dynamics and its role in pressure ulcers
Abstract
Pressure ulcers are a significant healthcare problem affecting the quality of life in wheelchair bounded or bed-ridden people and are a major cost to the healthcare system. Various assessment tools such as the Braden scale have been developed to quantify the risk level of pressure ulcers. These tools have provided an initial guideline on preventing pressure ulcers while additional assessments are needed to improve the outcomes of pressure ulcer prevention. Skin blood flow function that determines the ability of the skin in response to ischemic stress has been proposed to be a good indicator for identifying people at risk of pressure ulcers. Wavelet spectral and nonlinear complexity analyses have been performed to investigate the influences of the metabolic, neurogenic and myogenic activities on microvascular regulation in people with various pathological conditions. These findings have contributed to the understanding of the role of ischemia and viability on the development of pressure ulcers. The purpose of the present review is to provide an introduction of the basic concepts and approaches for the analysis of skin blood flow oscillations, and present an overview of the research results obtained so far. We hope this information may contribute to the development of better clinical guidelines for the prevention of pressure ulcers.
Copyright © 2013 Tissue Viability Society. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no commercial relationships which may lead to a conflict of interest with any of the authors.
Figures
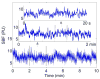
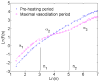
Similar articles
-
Relationship between nonlinear properties of sacral skin blood flow oscillations and vasodilatory function in people at risk for pressure ulcers.Microvasc Res. 2010 Jul;80(1):44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2010.03.009. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Microvasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20347852
-
Wavelet analysis of sacral skin blood flow oscillations to assess soft tissue viability in older adults.Microvasc Res. 2009 Sep;78(2):162-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2009.05.004. Epub 2009 May 22. Microvasc Res. 2009. PMID: 19465031
-
Local cooling reduces skin ischemia under surface pressure in rats: an assessment by wavelet analysis of laser Doppler blood flow oscillations.Physiol Meas. 2012 Oct;33(10):1733-45. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/33/10/1733. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Physiol Meas. 2012. PMID: 23010955 Free PMC article.
-
Pressure ulcer prevention.J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2004;14(4):285-304. doi: 10.1615/jlongtermeffmedimplants.v14.i4.20. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2004. PMID: 15447627 Review.
-
The effects of massage as a method to prevent pressure ulcers. A review of the literature.Ostomy Wound Manage. 2005 Apr;51(4):70-80. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2005. PMID: 16089061 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic Responses of Human Skin and Fascia to an Innovative Stimulation Device-Shear Wave Stimulation.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Aug 6;9(8):475. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9080475. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194454 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between predisposing and facilitating factors: Does it influence the risk of developing peri-operative pressure injuries?Int Wound J. 2022 Dec;19(8):2082-2091. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13811. Epub 2022 Apr 3. Int Wound J. 2022. PMID: 35373448 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of erythropoietin against pressure ulcer in a mouse model of small fiber neuropathy.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 25;9(11):e113454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113454. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25422898 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of peak pressure index parameters for people with spinal cord injury using wheelchair tilt-in-space and recline: methodology and preliminary report.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:508583. doi: 10.1155/2014/508583. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25057491 Free PMC article.
-
Wavelet Phase Coherence Analysis of Oxyhemoglobin and DeoxyHemoglobin Oscillations to Investigate the Relationship Between Cups of Cupping Therapy.J Biophotonics. 2025 Jan;18(1):e202400337. doi: 10.1002/jbio.202400337. Epub 2024 Nov 8. J Biophotonics. 2025. PMID: 39512092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reddy M, Gill SS, Rochon PA. Preventing pressure ulcers: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(8):974–84. - PubMed
-
- Chen D, Apple DF, Jr, Hudson LM, Bode R. Medical complications during acute rehabilitation following spinal cord injury--current experience of the Model Systems. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80(11):1397–401. - PubMed
-
- Brem H, Lyder C. Protocol for the successful treatment of pressure ulcers. Am J Surg. 2004;188(1A Suppl):9–17. - PubMed
-
- Jan YK, Brienza DM. Technology for pressure ulcer prevention. Topics in Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation. 2006;11(4):30–41.
-
- Bergstrom N, Braden BJ, Laguzza A, Holman V. The Braden Scale for Predicting Pressure Sore Risk. Nursing Reasearch. 1987;36(4):205–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

