A C. elegans screening platform for the rapid assessment of chemical disruption of germline function
- PMID: 23603051
- PMCID: PMC3672921
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1206301
A C. elegans screening platform for the rapid assessment of chemical disruption of germline function
Abstract
Background: Despite the developmental impact of chromosome segregation errors, we lack the tools to assess environmental effects on the integrity of the germline in animals.
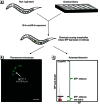
Objectives: We developed an assay in Caenorhabditis elegans that fluorescently marks aneuploid embryos after chemical exposure.
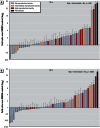
Methods: We qualified the predictive value of the assay against chemotherapeutic agents as well as environmental compounds from the ToxCast Phase I library by comparing results from the C. elegans assay with the comprehensive mammalian in vivo end point data from the ToxRef database.
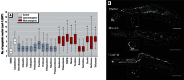
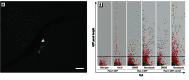
Results: The assay was highly predictive of mammalian reproductive toxicities, with a 69% maximum balanced accuracy. We confirmed the effect of select compounds on germline integrity by monitoring germline apoptosis and meiotic progression.
Conclusions: This C. elegans assay provides a comprehensive strategy for assessing environmental effects on germline function.
Conflict of interest statement
The content is the authors’ responsibility and does not necessarily represent the views of the NIEHS or NIH.
P.A. and M.P.C. have a patent application on the technology described here. The other authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Colaiácovo MP. The many facets of SC function during C. elegans meiosis. Chromosoma. 2006;115:195–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

