Stepwise protein folding at near amino acid resolution by hydrogen exchange and mass spectrometry
- PMID: 23603271
- PMCID: PMC3651421
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1305887110
Stepwise protein folding at near amino acid resolution by hydrogen exchange and mass spectrometry
Abstract
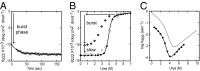
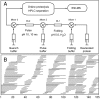
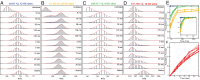
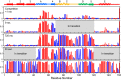
The kinetic folding of ribonuclease H was studied by hydrogen exchange (HX) pulse labeling with analysis by an advanced fragment separation mass spectrometry technology. The results show that folding proceeds through distinct intermediates in a stepwise pathway that sequentially incorporates cooperative native-like structural elements to build the native protein. Each step is seen as a concerted transition of one or more segments from an HX-unprotected to an HX-protected state. Deconvolution of the data to near amino acid resolution shows that each step corresponds to the folding of a secondary structural element of the native protein, termed a "foldon." Each folded segment is retained through subsequent steps of foldon addition, revealing a stepwise buildup of the native structure via a single dominant pathway. Analysis of the pertinent literature suggests that this model is consistent with experimental results for many proteins and some current theoretical results. Two biophysical principles appear to dictate this behavior. The principle of cooperativity determines the central role of native-like foldon units. An interaction principle termed "sequential stabilization" based on native-like interfoldon interactions orders the pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chamberlain AK, Handel TM, Marqusee S. Detection of rare partially folded molecules in equilibrium with the native conformation of RNaseH. Nat Struct Biol. 1996;3(9):782–787. - PubMed
-
- Raschke TM, Marqusee S. The kinetic folding intermediate of ribonuclease H resembles the acid molten globule and partially unfolded molecules detected under native conditions. Nat Struct Biol. 1997;4(4):298–304. - PubMed
-
- Raschke TM, Kho J, Marqusee S. Confirmation of the hierarchical folding of RNase H: A protein engineering study. Nat Struct Biol. 1999;6(9):825–831. - PubMed
-
- Cecconi C, Shank EA, Bustamante C, Marqusee S. Direct observation of the three-state folding of a single protein molecule. Science. 2005;309(5743):2057–2060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

