Blunted HPA axis response to stress is related to a persistent Dysregulation Profile in youth
- PMID: 23603315
- PMCID: PMC3714851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2013.04.002
Blunted HPA axis response to stress is related to a persistent Dysregulation Profile in youth
Abstract
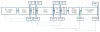
The Child Behavior Checklist Dysregulation Profile (DP) in youth has been shown to be a predictor of psychopathology later in life. We examined the activity of the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis in youth with remitted, new, persistent, and no DP. Data from 489 youth (47% boys) participating in a Dutch longitudinal general population study were included (Wave 1 mean age=11.5, Wave 2=14.2). Wave 2 diurnal cortisol patterns and levels in response to a laboratory stress paradigm were compared in youth with DP at Wave 1 only, Wave 2 only, both Waves, and neither Wave. Youth with the DP at Wave 2 only or at both time points showed blunted cortisol responses to stress relative to the other two groups. There were no group or sex differences in diurnal cortisol activity. More research is needed to determine how the association between DP symptoms and HPA axis functioning changes over time.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Aardal E, Holm AC. Cortisol in saliva - Reference ranges and relation to cortisol in serum. European Journal of Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry. 1995;33:927–932. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms and Profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont Center for Children, Youth, and Families; 2001.
-
- Althoff RR, Rettew DC, Faraone SV, Boomsma DI, Hudziak JJ. Latent class analysis shows strong heritability of the child behavior checklist-juvenile bipolar phenotype. [Comparative Study Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t] Biological psychiatry. 2006;60(9):903–911. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.02.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Althoff RR, Verhulst FC, Rettew DC, Hudziak JJ, van der Ende J. Adult outcomes of childhood dysregulation: a 14-year follow-up study. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural] Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2010;49(11):1105–1116. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2010.08.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

