Mutations in Escherichia coli ExbB transmembrane domains identify scaffolding and signal transduction functions and exclude participation in a proton pathway
- PMID: 23603742
- PMCID: PMC3697263
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00017-13
Mutations in Escherichia coli ExbB transmembrane domains identify scaffolding and signal transduction functions and exclude participation in a proton pathway
Abstract
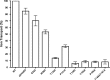
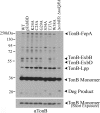
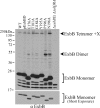
The TonB system couples cytoplasmic membrane proton motive force (pmf) to active transport of diverse nutrients across the outer membrane. Current data suggest that cytoplasmic membrane proteins ExbB and ExbD harness pmf energy. Transmembrane domain (TMD) interactions between TonB and ExbD allow the ExbD C terminus to modulate conformational rearrangements of the periplasmic TonB C terminus in vivo. These conformational changes somehow allow energization of high-affinity TonB-gated transporters by direct interaction with TonB. While ExbB is essential for energy transduction, its role is not well understood. ExbB has N-terminus-out, C-terminus-in topology with three TMDs. TMDs 1 and 2 are punctuated by a cytoplasmic loop, with the C-terminal tail also occupying the cytoplasm. We tested the hypothesis that ExbB TMD residues play roles in proton translocation. Reassessment of TMD boundaries based on hydrophobic character and residue conservation among distantly related ExbB proteins brought earlier widely divergent predictions into congruence. All TMD residues with potentially function-specific side chains (Lys, Cys, Ser, Thr, Tyr, Glu, and Asn) and residues with probable structure-specific side chains (Trp, Gly, and Pro) were substituted with Ala and evaluated in multiple assays. While all three TMDs were essential, they had different roles: TMD1 was a region through which ExbB interacted with the TonB TMD. TMD2 and TMD3, the most conserved among the ExbB/TolQ/MotA/PomA family, played roles in signal transduction between cytoplasm and periplasm and the transition from ExbB homodimers to homotetramers. Consideration of combined data excludes ExbB TMD residues from direct participation in a proton pathway.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The ExbD periplasmic domain contains distinct functional regions for two stages in TonB energization.J Bacteriol. 2012 Jun;194(12):3069-77. doi: 10.1128/JB.00015-12. Epub 2012 Apr 6. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22493019 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the ExbB cytoplasmic carboxy terminus prevent energy-dependent interaction between the TonB and ExbD periplasmic domains.J Bacteriol. 2011 Oct;193(20):5649-57. doi: 10.1128/JB.05674-11. Epub 2011 Aug 12. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21840979 Free PMC article.
-
His(20) provides the sole functionally significant side chain in the essential TonB transmembrane domain.J Bacteriol. 2007 Apr;189(7):2825-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.01925-06. Epub 2007 Feb 2. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17277053 Free PMC article.
-
Energization of Outer Membrane Transport by the ExbB ExbD Molecular Motor.J Bacteriol. 2023 Jun 27;205(6):e0003523. doi: 10.1128/jb.00035-23. Epub 2023 May 23. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37219427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substrate Uptake by TonB-Dependent Outer Membrane Transporters.Mol Microbiol. 2024 Dec;122(6):929-947. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15332. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Mol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39626085 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ExbB cytoplasmic loop deletions cause immediate, proton motive force-independent growth arrest.J Bacteriol. 2013 Oct;195(20):4580-91. doi: 10.1128/JB.00334-13. Epub 2013 Aug 2. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23913327 Free PMC article.
-
The Intrinsically Disordered Region of ExbD Is Required for Signal Transduction.J Bacteriol. 2020 Mar 11;202(7):e00687-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00687-19. Print 2020 Mar 11. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31932309 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Stoichiometry of the Ton Molecular Motor.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 7;21(2):375. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020375. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31936081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Water Disinfection Byproducts Induce Antibiotic Resistance-Role of Environmental Pollutants in Resistance Phenomena.Environ Sci Technol. 2016 Mar 15;50(6):3193-201. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b05113. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Environ Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 26928861 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structures of the E. coli Ton and Tol motor complexes.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5506. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61286-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40595649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krewulak KD, Vogel HJ. 2011. TonB or not TonB: is that the question? Biochem. Cell Biol. 89:87–97 - PubMed
-
- Zimbler DL, Penwell WF, Gaddy JA, Menke SM, Tomaras AP, Connerly PL, Actis LA. 2009. Iron acquisition functions expressed by the human pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii. Biometals 22:23–32 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

