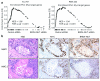
Figure 2. The acetyl-histone binding of BRD4-NUT’s bromodomains are required for the expression of MYC in NMC
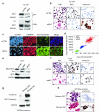
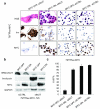
(a) BRD4-NUT enrichment at the MYC promoter region requires its bromodomains. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) using 20 uL of anti-NUT (BX.1, whole rabbit serum) antibody in TC-797 cells treated with vehicle (DMSO) or the acetyl-histone mimic bromodomain inhibitor (BETi), JQ1 (500 nM (4)), for four hours. Samples were subjected to ChIP using the SimpleChIP Chromatin IP Kit from Cell Signaling Technologies (Danvers, MA). For each IP, 4 × 107 cells were crosslinked with 1% formaldehyde for ten minutes at 37°C and nuclei were digested with micrococcal nuclease as per manufacturer instructions, with the exception that the “high salt” wash was at 200 mM NaCl. ChIPd DNA was eluted in 200 ul. 4 ul of eluted DNA was subjected to quantitative PCR (qPCR), in triplicate, using primers (Supplemental Table 1) designed to amplify the promoter-proximal region of MYC, and created based on distance from the transcriptional start site (TSS). qPCR was performed on a Bio-Rad iCycler in 96 well plate format with IQ SYBR Green supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). Amplification curves and Ct values were generated using MyiQ Single-Color Real-Time software (Bio-Rad) using a range of inputs (10%, 0.1%, and 0.01%) to generate the standard curve. Results are depicted as percent input, and are representative of one of three separate experiments with standard deviations shown. Amino acids 800-1000 of NUT were used as immunogen to make polyclonal rabbit BX.1 antibody, using methods as described (42) (Chemicon, Temecula, CA). Primers used are listed in Supplemental Table 1. (b) BRD4-NUT maintains MYC transcription. mRNA levels, as measured by quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR), of MYC, compared with those of the reference gene Ribosomal protein L13a (RPL13a), 24 h following siRNA-mediated knockdown of BRD4-NUT, or treatment with 500 nM JQ1. All qRT-PCR experiments are representative of triplicate qRT-PCRs from one of three independent experiments. Total RNA was harvested at the indicated time points using TRizol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). RNA (1 ug) was reversed transcribed into cDNA using the iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). RT-qPCR was performed in triplicate on a Bio-Rad iCycler in 96 well plate format with IQ SYBR Green supermix (Bio-Rad) and 1 uL of cDNA template per reaction. Amplification curves and Ct values were generated using MyiQ Single-Color Real-Time software (Bio-Rad). Primers used are listed in Supplemental Table 1. (c) Immunoblot reveals that treatment of TC-797 NMC cells with JQ1 (500 nM) rapidly decreases MYC levels. Antibodies used were rabbit anti-MYC (1;1000, #9402, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA) and anti-GAPDH. siRNA was transfected into 2.5×106 cells at a final concentration of 50 nM using the Nucleofector II (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) electroporator, as described (3). (d) BRD4-NUT is necessary for maintenance of MYC protein expression. Immunoblot of lysates from TC-797 cells 24 h following transfection with control siRNA (siCTRL, siGENOME non-targeting siRNA #4, Dharmacon, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) or siRNA directed at NUT (si3583, Dharmacon, sense, 5′ AAUUACCUUUGGAAGGAGCUAUU 3′, and anti-sense, 5′ UUUUAAUGGAAACCUUCCUCGAU 3′, oligonucleotides). Staining for BRD4-NUT was accomplished using AX.1 anti-NUT rabbit polyclonal antibody (1:500 (42)). (e) Schematic of BRD4-NUT, including known functional domains. (f-h) The acetyl-histone-binding bromodomains of BRD4-NUT are required for the blockade of differentiation and maintenance of MYC expression. (f) Immunophenotypic and morphologic (H&E) changes reveal differentiation in 797TRex-flag-BD12 cells expressing wild type tandem bromodomains 1 and 2 (wtBD12), but not when point mutations of key acetyl-histone binding residues are present in either or both bromodomains (N140A is the key acetyl-histone binding residue of bromodomain 1 (BD1), and N433A is that of bromodomain 2 (BD2)) of the tandem bromodomain construct (BD12), 120 h following induction. Differentiation is evidenced by morphologic (H&E) flattening and marked enlargement, and by increased expression of involucrin. (g) Immunoblot of lysates from 797TRex NMC cells 120h following tetracycline-induced expression (“OFF” is vehicle (ethanol) treated, and “ON” is tetracycline treated) of the dual flag-tagged tandem bromodomains (BD12) of BRD4, with and without (wt) point mutations that abrogate acetylhistone binding, demonstrates that only intact BD12 can induce differentiation, as evidenced by involucrin expression. Involucrin is a marker of squamous differentiation. Lysates 120 h after addition of tetracycline or ethanol were prepared with high-salt RIPA buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 8.0, containing 1% NP-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 250 mM NaCl, and 5 mM EDTA) and separated by SDS-PAGE, electrophoretically transferred to Immobilon membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA), and stained with mouse anti-GAPDH (1:5000, 6C5, Life Technologies/ Ambion, Grand Island, NY), mouse anti-flag (1:1000, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), and mouse anti-Involucrin (1:500, Sigma-Aldrich). Staining was developed using a chemiluminescent method (SuperSignal, West Pico; Pierce, Rockford, IL). The NMC cell line, TC-797, has been described (43). A TRex derivative of the NMC cell line, TC-797, containing a single FLP recombinase site (FRT), and multiple copies of tetracycline repressor gene (TR), to allow for the isogenic insertion of a desired tetracycline(tet)-inducible transgene, was created using the Flp-In T-Rex Core Kit and the pLenti6-TR plasmid, according the manufacturer’s instructions (Invitrogen). This derivative is termed 797TRex. Tetracycline-inducible 797TRex subclones were created according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) by cotransfection of TC-797 TRex cells (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) with pCAGGS_FLPe and pcDNA5-Frt-TO plasmids encoding the following flag-epitope tagged polypeptides: BRD4 bromodomains 1 and 2 (BD12, residues 39-457 of BRD4); and BD12 with the point substitutions of the critical acetyl-histone-binding amino acids, N140A and N433A, alone or in combination(12). Clones were selected using Hygromycin (Invitrogen). Primers used to create these cDNAs and oligonucleotides used for site-directed mutagenesis (Stratagene/ Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA) are provided in Supplemental Table 1. (h) Immunoblot revealing that induction of flag-wtBD12 results in decreased MYC protein levels.